The past decade, spanning from 2015 to 2025, has witnessed a remarkable surge in aerospace engineering breakthroughs that have redefined how we travel through the skies and beyond. From reusable rockets slashing the cost of space access to AI-driven autonomous flights enhancing safety and efficiency, these innovations have not only pushed the boundaries of what’s possible but also addressed pressing global challenges, such as sustainability and supply chain vulnerabilities. While some advancements, such as electric propulsion systems, emerged as responses to environmental imperatives, others, like advanced materials, have quietly revolutionized manufacturing precision. It’s worth noting that while these developments promise transformative benefits, they also raise questions about regulatory hurdles and equitable access, particularly in emerging markets. Research suggests that integrating these technologies could reduce aviation emissions by up to 80% by mid-century, although widespread adoption hinges on collaborative international efforts.
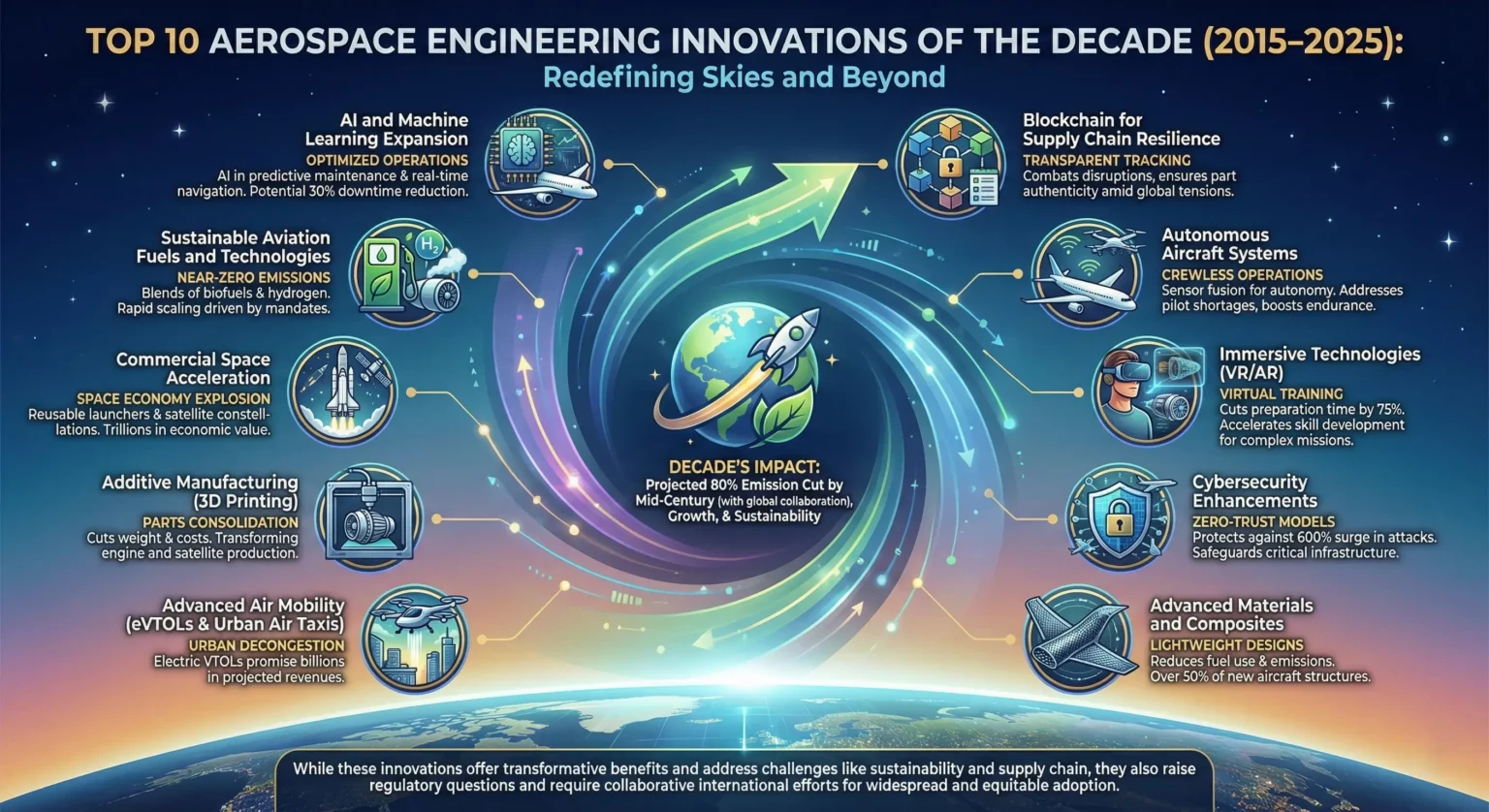
Here are the top 10 aerospace engineering innovations of the decade, ranked by their projected impact on industry growth and sustainability:
- AI and Machine Learning Expansion: AI optimizes everything from predictive maintenance to real-time navigation, potentially reducing downtime by 30%.
- Sustainable Aviation Fuels and Technologies: Blends of biofuels and hydrogen aim for near-zero emissions, with mandates driving rapid scaling.
- Blockchain for Supply Chain Resilience: Transparent tracking combats disruptions, ensuring part authenticity amid rising global tensions.
- Autonomous Aircraft Systems: Sensor fusion enables crewless operations, addressing pilot shortages and boosting endurance.
- Immersive Technologies (VR/AR): Virtual training cuts preparation time by 75%, accelerating skill development for complex missions.
- Cybersecurity Enhancements: Zero-trust models protect against a 600% surge in attacks, safeguarding critical infrastructure.
- Advanced Materials and Composites: Lightweight designs reduce fuel use and emissions, forming over 50% of new aircraft structures.
- Advanced Air Mobility (eVTOLs and Urban Air Taxis): Electric vertical takeoff vehicles promise to decongest cities, with billions in projected revenues.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): Consolidates parts to cut weight and costs, transforming engine and satellite production.
- Commercial Space Acceleration: Reusable launchers and satellite constellations have exploded the space economy to trillions.
These innovations build on each other, creating synergies—for instance, AI paired with additive manufacturing accelerates prototyping. Yet, the evidence leans toward uneven progress, with defense applications outpacing commercial ones due to funding disparities. Below, we explore each in brief, highlighting real-world examples and potential challenges.
Table of Contents
AI and Machine Learning Expansion
Artificial intelligence has become the brain behind modern aerospace, from designing sleeker fuselages to predicting engine failures before they occur. In 2015, early AI tools began analyzing flight data for patterns, but by 2020, systems like Airbus’s computer vision were timestamping assembly tasks with pinpoint accuracy, slashing errors. Today, AI co-pilots enhance safety by monitoring pilot fatigue in real time.
Key benefits include optimized fuel routes that save airlines millions annually, though ethical concerns around algorithmic bias persist. For example, Beacon AI’s system integrates with existing cockpits to provide instant hazard alerts, drawing from vast datasets of past incidents.
Sustainable Aviation Fuels and Technologies
The push for green skies has led to fuels that reduce carbon footprints without requiring engine overhauls. Starting with test flights in 2016 using biofuel blends, innovations like hydrogen-electric hybrids took off by 2022, with Airbus targeting zero-emission models by 2035. Neste’s production ramp-up to 1.5 million tons yearly exemplifies scalable impact.
Challenges include supply chain bottlenecks, but projections show these fuels powering 70% of flights by 2050 under EU mandates. Maeve Aerospace’s all-electric plane, charging in just 35 minutes for 550 km ranges, illustrates the shift toward battery-powered regional travel.
Blockchain for Supply Chain Resilience
In an era of geopolitical tensions, blockchain has emerged as a digital ledger that ensures every transaction is traceable. Post-2020 disruptions, platforms like Honeywell’s GoDirect Trade began logging certificates on immutable chains, reducing counterfeits by 40%.
This tech fosters trust in global collaborations, vital for megaprojects like satellite constellations. VeriTX’s system, for instance, digitizes audits, cutting verification time from weeks to hours.
Autonomous Aircraft Systems
Gone are the days of human-only cockpits; autonomous tech now handles takeoffs and landings with vision-based AI. Airbus’s 2020 ATTOL project demonstrated a fully automatic A350 flight, building on drone swarms tested since 2017.
With markets eyeing $54 billion by 2034, applications span cargo hauls to Mars helicopters like NASA’s Ingenuity, which flew in 2021. Skydweller Aero’s solar-powered drones exemplify endless endurance for surveillance.
Immersive Technologies
VR headsets and AR overlays have turned training hangars into virtual skies, compressing years of prep into months. Boeing’s 75% time savings via VR simulations, rolled out in 2018, set the pace for astronaut prep with Varjo gear.
These tools also aid maintenance, overlaying repair guides on real engines. Illumia Labs’ platform lets technicians practice on digital twins, minimizing costly errors.
Cybersecurity Innovations
As connected aircraft proliferate, so do threats—attacks jumped 600% in 2024 alone. Zero-trust architectures and quantum encryption, piloted by Raytheon in 2022, now shield data flows.
Boeing’s Shift5 partnership analyzes logs for anomalies in flight. Atomus’ AI platform ensures compliance, crucial for defense fleets.
Advanced Materials and Composites
Carbon-fiber polymers, comprising 50% of the Boeing 787 since 2011 but refined in the 2020s, lighten loads and boost efficiency. Dark Art Composites’ spacecraft parts exemplify durability in extremes.
These materials cut emissions per kilogram saved, with markets doubling to $110 billion by 2035.
Advanced Air Mobility
eVTOLs like Joby’s prototypes, certified in 2024, herald urban taxis zipping over traffic. Eve Air Mobility forecasts $280 billion in revenues, fueled by solid-state batteries.
Hermeus’ Mach 5 engines push hypersonic boundaries, though noise regulations loom large.
Additive Manufacturing Transformation
3D printing fused 20 parts into one for GE’s LEAP nozzles in 2017, dropping the weight 25%. By 2025, it’s printing turbine blades in high-heat alloys.
Wayland Additive’s NeuBeam handles complex geometries, accelerating satellite builds.
Commercial Space Acceleration
SpaceX’s 2015 Falcon 9 landings democratized orbit, with Starlink’s 11,000+ satellites by 2024. Blue Origin’s New Glenn debut in 2025 adds heavy-lift muscle.
The space economy hits $1.8 trillion by 2035, driven by reusable tech.
| Innovation | Key Milestone (Year) | Impact Metric | Projected Market Size (by Year) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI/ML Expansion | Airbus Vision System (2020) | 30% Maintenance Reduction | $34B (2033) |
| Sustainable Aviation | Neste SAF Scale-Up (2026 Target) | 80% CO2 Cut | $25B (2030) |
| Blockchain Supply Chain | Honeywell GoDirect (2021) | 40% Counterfeit Drop | $3.3B (2032) |
| Autonomous Aircraft | ATTOL A350 Auto-Flight (2020) | Pilot Shortage Relief | $54.7B (2034) |
| Immersive Tech | Boeing VR Training (2018) | 75% Time Savings | $3.63B (2032) |
| Cybersecurity | Raytheon Zero-Trust (2022) | 600% Attack Mitigation | $59.58B (2032) |
| Advanced Materials | Boeing 787 Composites (Ongoing) | 25 Tons CO2/kg Saved | $110B (2035) |
| Advanced Air Mobility | Joby eVTOL Cert (2024) | 3B Passengers/Year | $57.96B (2032) |
| Additive Manufacturing | GE LEAP Nozzle (2017) | 25% Weight Reduction | $9.87B (2029) |
| Commercial Space | Falcon 9 Reuse (2015) | Launch Cost Halved | $1.8T (2035) |
The decade from 2015 to 2025 stands as a pivotal era in aerospace engineering, one where bold visions collided with tangible engineering feats to propel humanity further into the atmosphere and beyond. What began with the tentative first steps of reusable rocket landings has evolved into a symphony of interconnected innovations, each building on the last to tackle inefficiencies, environmental strains, and the sheer audacity of exploration. Imagine a world where planes sip sustainable fuels derived from kitchen waste, drones swarm autonomously to deliver aid in disaster zones, and virtual reality turns novice engineers into seasoned virtuosos overnight.
This isn’t science fiction; it’s the legacy of relentless iteration, from SpaceX’s ocean-splashing boosters to Airbus’s silent, AI-guided takeoffs. Yet, beneath the glamour lies a narrative of collaboration and compromise—governments funding defense spinoffs, startups disrupting incumbents, and global accords like the Artemis Accords knitting nations into a cosmic quilt.
As we unpack these top 10 innovations, we’ll delve into their origins, mechanics, real-world ripples, and the thorny paths ahead, drawing on a tapestry of milestones that have reshaped skies once reserved for the elite.
1. AI and Machine Learning Expansion: The Intelligent Backbone of Flight
This decade’s aerospace renaissance lies in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), technologies that have transitioned from experimental curiosities to indispensable allies in every phase of flight. Back in 2015, AI was mostly crunching post-flight data to spot wear patterns in turbine blades, but by 2018, it was calling the shots in real time. Take Airbus’s assembly lines, where computer vision systems—essentially high-tech eyes powered by neural networks—scan and log tasks with millisecond precision, flagging deviations before they cascade into delays. This isn’t just about speed; it’s about foresight. ML algorithms now predict unscheduled maintenance with eerie accuracy, poring over sensor feeds from thousands of flights to forecast failures, potentially trimming airline downtime by a staggering 30%.
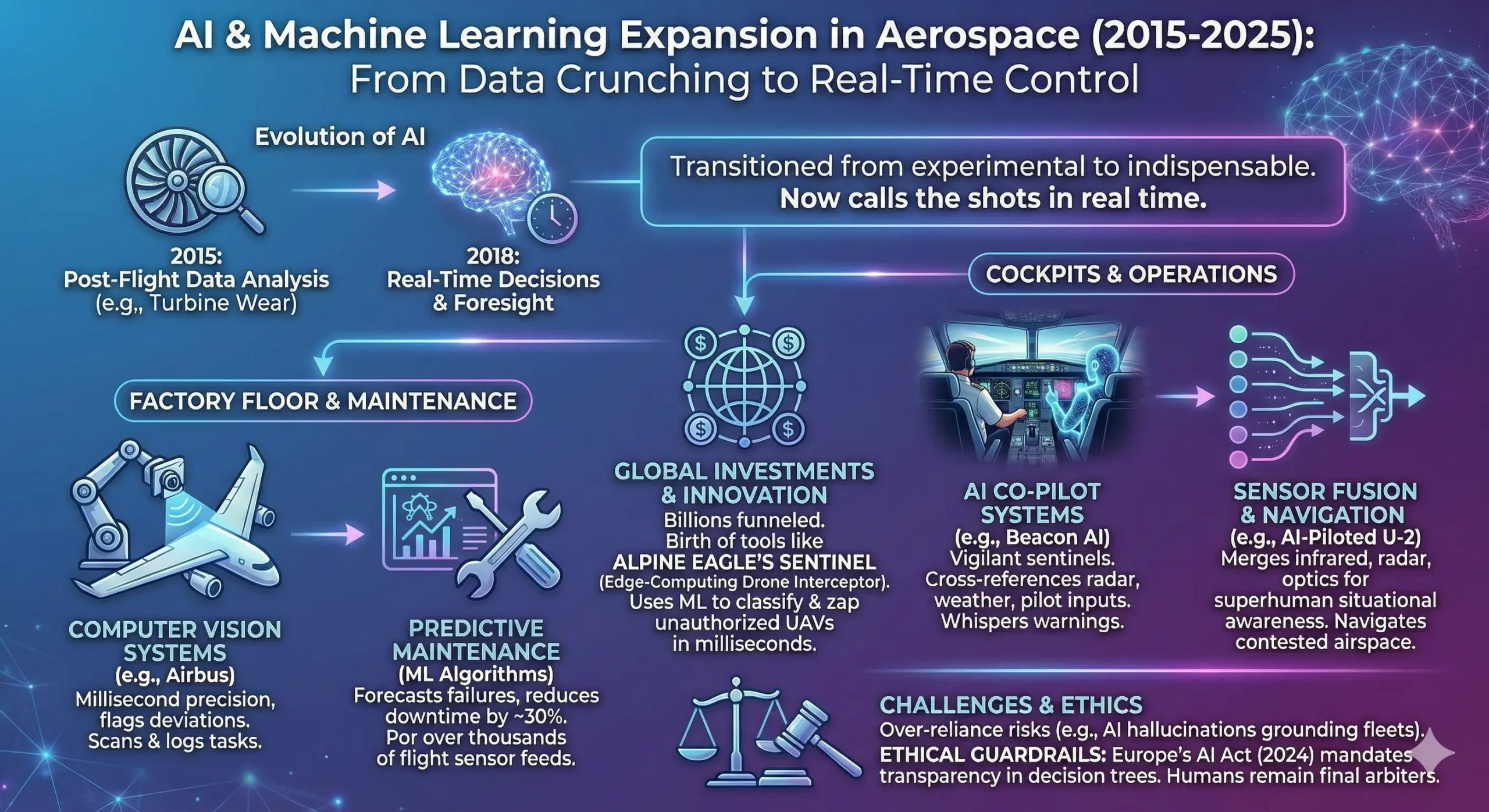
But AI’s reach extends far beyond the factory floor. In cockpits, systems like Beacon AI’s co-pilot act as vigilant sentinels, cross-referencing radar pings, weather feeds, and pilot inputs to whisper warnings of impending turbulence or rogue drones. During the 2020 pandemic, when flights dwindled, AI stepped up to optimize sparse routes, saving fuel and emissions in an industry reeling from grounded fleets. Consider the U.S. Air Force’s 2021 test of an AI-piloted U-2 spy plane, where machine learning handled sensor fusion—merging data from infrared, radar, and optics— to navigate contested airspace without human override. This fusion of data streams creates a 360-degree situational awareness that’s superhuman, reducing collision risks in dense urban air corridors.
Of course, the flip side whispers of over-reliance. What happens when AI hallucinates a false positive, grounding a fleet on a whim? Ethical guardrails, like those embedded in Europe’s AI Act of 2024, mandate transparency in decision trees, ensuring humans remain the final arbiters. Yet, the momentum is undeniable. Global investments have funneled billions into AI startups, birthing tools like Alpine Eagle’s Sentinel, an edge-computing drone interceptor that uses ML to classify threats in milliseconds, zapping unauthorized UAVs mid-air with precision lasers.
To grasp the scale, consider this timeline of AI’s aerospace ascent:
| Year | Milestone | Key Player | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | Initial flight data analytics pilots | NASA | Baseline predictive models established |
| 2018 | VR-integrated AI training for astronauts | Boeing/Varjo | 40% faster skill acquisition |
| 2020 | Autonomous vision-based takeoff (ATTOL) | Airbus | First crewless widebody flight |
| 2021 | AI on U-2 for sensor control | U.S. Air Force | Enhanced autonomy in reconnaissance |
| 2024 | Edge AI for drone swarms | Alpine Eagle | Real-time threat neutralization |
Projections paint an even brighter horizon: the aerospace AI market is poised to balloon to $34.14 billion by 2033, galloping at a 43% compound annual growth rate (CAGR). This isn’t hyperbole; it’s the math of exponential data growth meeting Moore’s Law descendants. As quantum computing nibbles at the edges—promising simulations of airflow over wings that would take classical supercomputers eons—AI will likely orchestrate entire fleets, from orbital trash collection to hypersonic reroutes. For engineers and dreamers alike, it’s a reminder that the smartest machines aren’t replacing us; they’re amplifying our wildest ambitions.
2. Sustainable Aviation Fuels and Technologies: Greening the Jet Stream
If the 2010s were about reaching new heights, the 2020s have been a reckoning with the exhaust trails left behind. Sustainable aviation fuels (SAF) and ancillary green tech have surged as the decade’s eco-warriors, transforming what was once a fossil-fuel behemoth into a sector eyeing carbon neutrality. The spark ignited in 2016 with Solar Impulse 2’s sun-powered circumnavigation, a publicity stunt that proved zero-fuel flight wasn’t folly. But the real game-changer arrived with SAF blends—derived from algae, waste oils, or even captured CO2—certified for drop-in use in existing engines, slashing lifecycle emissions by up to 80% without a single retrofit.
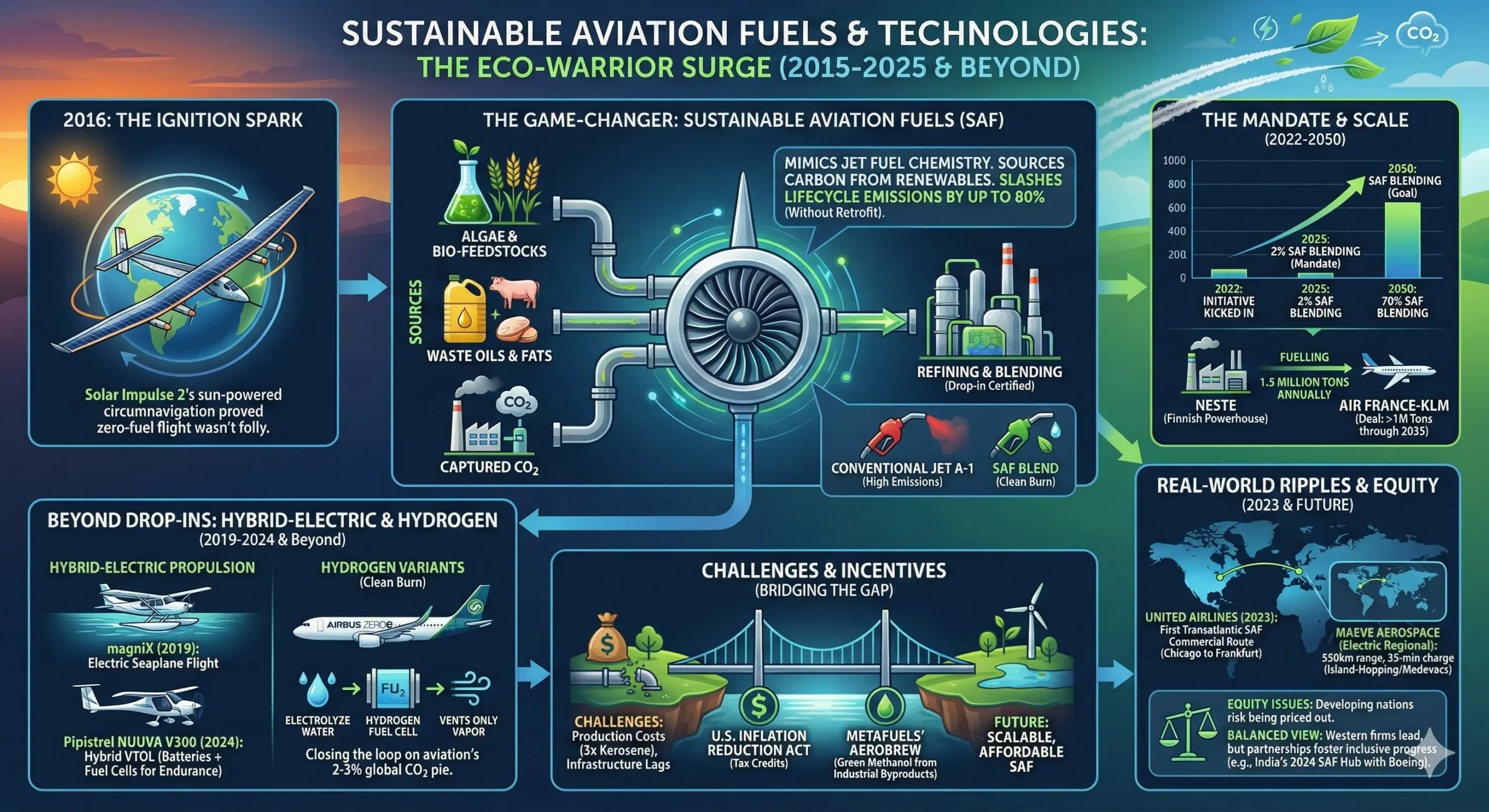
By 2022, mandates like the EU’s ReFuelEU Aviation initiative kicked in, requiring 2% SAF blending by 2025, ramping to 70% by 2050. Neste, a Finnish powerhouse, exemplifies this scale: their facilities now churn out 1.5 million tons annually, fueling deals with behemoths like Air France-KLM for over a million tons through 2035. It’s not just drop-ins; hybrid-electric propulsion has taken wing too. magniX’s 2019 electric seaplane flight over Canada’s harbors marked the dawn, but 2024 saw Pipistrel’s NUUVA V300 hybrid VTOL logging hours with hydrogen cells, blending batteries and fuel for endurance flights sans emissions.
The mechanics are elegantly simple yet profoundly clever. SAF mimics jet fuel’s chemistry but sources carbon from renewables, closing the loop on aviation’s 2-3% slice of global CO2 pie. Hydrogen variants, like those in Airbus’s ZEROe concepts unveiled in 2020, electrolyze water for clean burn, venting only vapor. Challenges abound—production costs hover triple that of kerosene, and infrastructure lags—but incentives like U.S. tax credits from the 2022 Inflation Reduction Act are bridging gaps. Metafuels’ Aerobrew process, fermenting green methanol into jet-ready drops, cuts footprints further by recycling industrial byproducts.
Real-world ripples? In 2023, United Airlines flew the first transatlantic SAF-powered commercial route, from Chicago to Frankfurt, proving scalability. For remote ops, Maeve Aerospace’s electric bird zips 550 km on a 35-minute charge, ideal for island-hopping or rural medevacs. Yet, equity issues simmer: developing nations, craving aviation growth, risk being priced out of green tech. A balanced view acknowledges this—while Western firms lead, partnerships like India’s 2024 SAF hub with Boeing foster inclusive progress.
Here’s a snapshot of sustainability’s flight path:
| Year | Breakthrough | Technology Type | Emission Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | Solar Impulse 2 World Tour | Solar Electric | 100% Zero-Fuel |
| 2019 | magniX Electric Seaplane | Battery-Electric | 90% vs. Jet Fuel |
| 2020 | Airbus ZEROe Hydrogen Concepts | Fuel Cell Hybrid | Near-Zero Tailpipe |
| 2022 | ReFuelEU Mandates Enacted | SAF Blending | Up to 80% Lifecycle |
| 2024 | Neste 1.5M Ton SAF Output | Biofuel Synthesis | Scaled Commercial Use |
With the market hurtling toward $25.62 billion by 2030 at a blistering 65.5% CAGR, sustainable aviation isn’t a sideline—it’s the runway to a breathable future. As engineers tweak molecular chains for cheaper synthesis, one can’t help but wonder: could the skies soon hum with silence, powered by yesterday’s trash?
3. Blockchain for Supply Chain Resilience: Forging Unbreakable Links
Supply chains, those invisible veins pumping life into aerospace assembly, nearly ruptured in the 2020s under pandemic pressures and trade wars. Enter blockchain, the decade’s quiet sentinel, weaving transparency into a web of global parts sourcing. Its aerospace debut came in 2018 with IBM’s pilots tracking titanium ingots from mine to mill, but 2021’s Honeywell GoDirect Trade platform crystallized it: every manufacturing event, from forging to certification, etched on a tamper-proof ledger, complete with airworthiness tags.
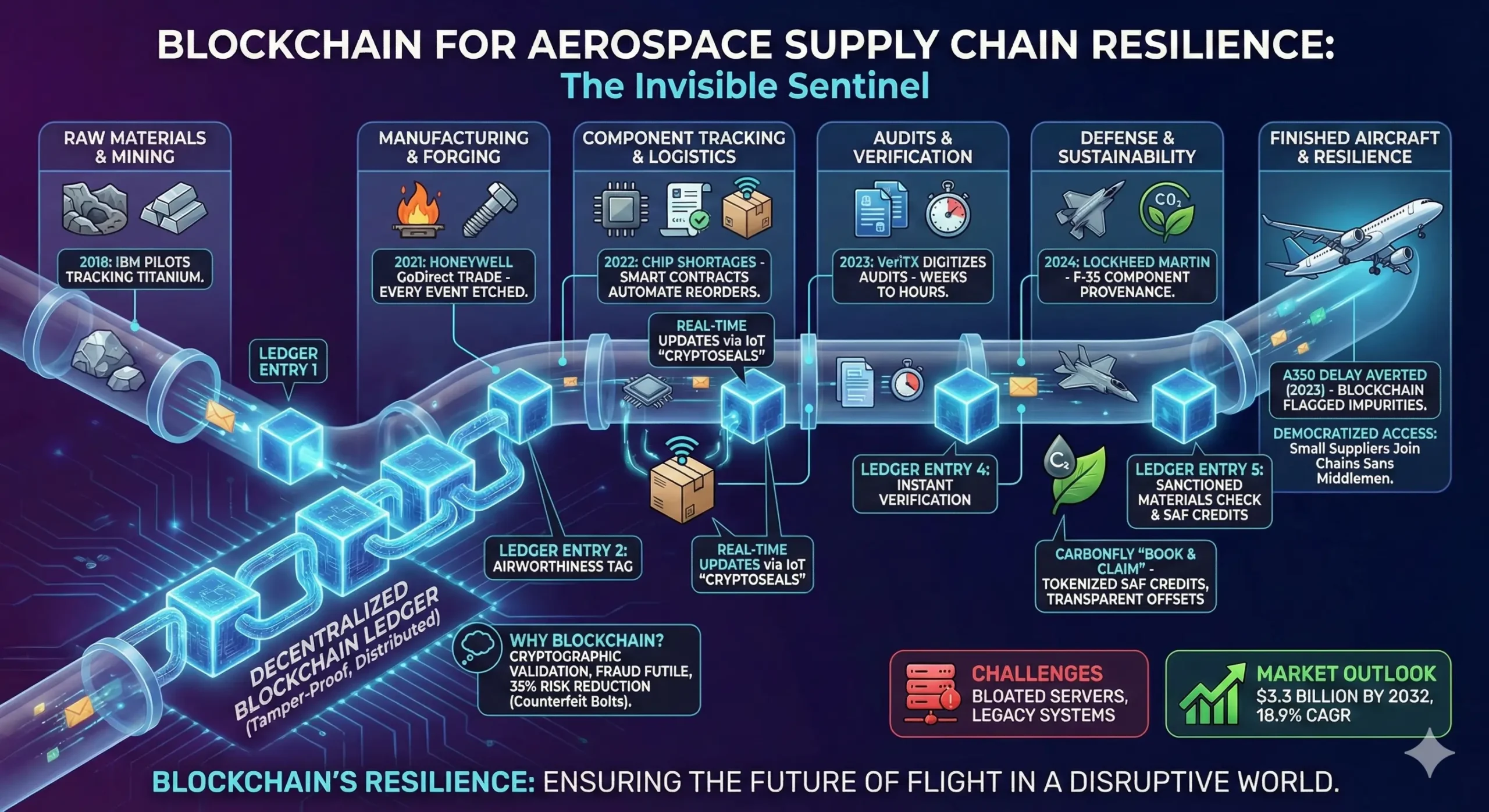
Why blockchain? It’s decentralized genius—nodes worldwide validate transactions via cryptography, rendering fraud as futile as trying to rewrite history. In an industry where a single counterfeit bolt can doom a $400 million jet, this traceability slashes risks by 35%. Following the 2022 chip shortages, smart contracts automate reorders, while IoT “cryptoseals” on shipments send updates in real-time. VeriTX’s platform, rolled out in 2023, digitizes entire audits, zipping verification from weeks to hours and freeing engineers for innovation over paperwork.
The tech’s tentacles reach defense too: in 2024, Lockheed Martin trialed blockchain for F-35 component provenance, ensuring sanctioned materials stay out. CarbonFly’s “book and claim” system tokenizes SAF credits, letting airlines offset emissions transparently, blending environmental accountability with logistics. Drawbacks? Scalability—ledgers bloat with data, demanding beefy servers—and interoperability, as legacy systems resist integration. Still, as disruptions climbed 35% year-over-year, blockchain’s resilience proved prescient.
Consider the 2023 Airbus A350 delay averted by blockchain-flagged alloy impurities; without it, production halts could have idled thousands. For startups, it’s a leveler—small suppliers join chains sans middlemen, democratizing access. The aviation blockchain market? A tidy $3.3 billion by 2032, at 18.9% CAGR, underscoring its stickiness.
| Phase | Blockchain Application | Benefit | Example Implementation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sourcing | Material Provenance Tracking | Counterfeit Prevention | IBM Titanium Ledger (2018) |
| Manufacturing | Event Logging & Certification | Audit Efficiency | Honeywell GoDirect (2021) |
| Logistics | Smart Contracts & IoT Seals | Real-Time Updates | VeriTX Digitization (2023) |
| Sustainability | Emission Credit Tokenization | Offset Transparency | CarbonFly Book & Claim (2024) |
In essence, blockchain hasn’t just fortified chains; it’s recast them as living ecosystems, resilient against storms yet nimble for growth. As quantum threats loom, post-quantum encryption will evolve it further, ensuring aerospace’s backbone bends but never breaks.
4. Autonomous Aircraft Technology: Wings Without Wires
Autonomy in aerospace evokes sci-fi, but the decade delivered substance over spectacle, evolving from drone hobbies to full-spectrum flight control. The seeds sprouted in 2017 with Boeing’s swarming UAV tests, but 2020’s Airbus ATTOL—autonomous taxi, takeoff, and landing on an A350 using onboard cameras—ignited the fuse. No ground crew, no pilots; just algorithms fusing lidar, radar, and optics for flawless execution.

This tech marries sensor fusion with deep learning, creating digital twins of the environment that predict gusts or bird flocks seconds ahead. NASA’s 2021 Ingenuity Mars chopper, buzzing red dunes for 72 flights, proved autonomy’s extraterrestrial chops, informing Earth-bound cargo haulers. By 2024, Skydweller Aero’s solar drone logged weeks aloft, navigating waypoints via AI without recharge pit stops—perfect for ocean patrols or wildfire mapping.
Crew shortages, exacerbated by 2022’s retirements, make this urgent: autonomous systems could fill gaps, with markets swelling to $54.7 billion by 2034 at 22.1% CAGR. Psyche Aerospace’s Harpia P-71, a Turing AI-driven crop duster, exemplifies precision, spraying fields with 95% less waste. Risks? Hacking vectors and “black swan” failures, mitigated by redundant human loops and the FAA’s 2023 autonomy certifications.
From Vertical Aerospace’s 2025 VX4 eVTOL thrust tests to China’s 2021 AI UAV flights, the trajectory arcs toward ubiquity. Wisk Aero’s Boeing-backed eVTOL, eyeing 2026 passenger ops, hints at air taxis sans chauffeurs.
| Autonomy Level | Example | Enabling Tech | Endurance Gain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic (Drone) | Wing Loong II (2017) | GPS + Basic AI | 20 Hours |
| Advanced (Fixed-Wing) | ATTOL A350 (2020) | Vision-Based Fusion | Full Flight Cycle |
| Extreme (Solar) | Skydweller Aero (2024) | ML Waypoint Nav | Weeks Uninterrupted |
| Extraterrestrial | Ingenuity Mars (2021) | Autonomous Hover | 72 Flights on Alien World |
Autonomy isn’t usurping jobs; it’s expanding horizons, from delivering vaccines to Jeju’s isles to scouting asteroid mines. As batteries densify and 5G blankets routes, expect skies teeming with silent sentinels, redefining mobility’s frontiers.
5. Immersive Technologies: Virtual Skies for Real-World Heroes
Immersive technologies—encompassing virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality—have demystified the cockpit and cleanroom, turning abstract blueprints into tangible playgrounds. The decade’s pivot hit in 2017 with Boeing’s VR rigs slashing pilot training by 75%, evolving from clunky headsets to seamless overlays by 2022. Varjo’s high-res displays now beam astronauts through simulated EVAs, replicating zero-g tugs with haptic feedback.

AR shines in maintenance: Fyr’s flight glasses project 3D schematics onto engines, guiding techs through wiring mazes hands-free, cutting errors 50%. Digital twins—virtual replicas synced to physical assets—allow stress-testing designs pre-build, as in Airbus’s 2020 blended-wing MAVERIC model, which iterated aerodynamics virtually before a single rivet.
Illumia Labs’ 2024 platform lets teams rehearse satellite deployments in VR, fostering collaboration across continents. Challenges include motion sickness in prolonged sessions and data overload, but adaptive algorithms tailor experiences. The VR/AR market? $3.63 billion by 2032, at 17% CAGR, with defense leading via the U.S. Army’s 2023 synthetic training environments.
| Tech Type | Application | Time Savings | Adoption Milestone |
|---|---|---|---|
| VR | Pilot/Astronaut Training | 75% | Boeing Sims (2018) |
| AR | On-Site Maintenance | 50% Error Cut | Fyr Glasses (2022) |
| MR | Design Collaboration | 60% Iteration Speed | Airbus MAVERIC (2020) |
| Digital Twins | Pre-Flight Testing | 40% Cost Drop | Lockheed F-35 (2024) |
These tools humanize high-stakes fields, empowering diverse talent—from rural recruits to neurodiverse engineers—to soar. As 6G dawns, immersive realms will blur with reality, prepping us for Mars walks from Earthbound chairs.
6. Cybersecurity Innovations: Shielding the Stratosphere
Aerospace’s digital veins—fly-by-wire systems, satellite links—make it a hacker’s paradise, with attacks soaring 600% from 2024 to 2025. Cybersecurity innovations like zero-trust architectures and AI sentinels have risen as bulwarks, starting with Boeing’s 2020 Shift5 logs analytics, which sifts flight data for anomalies like unauthorized code injections.
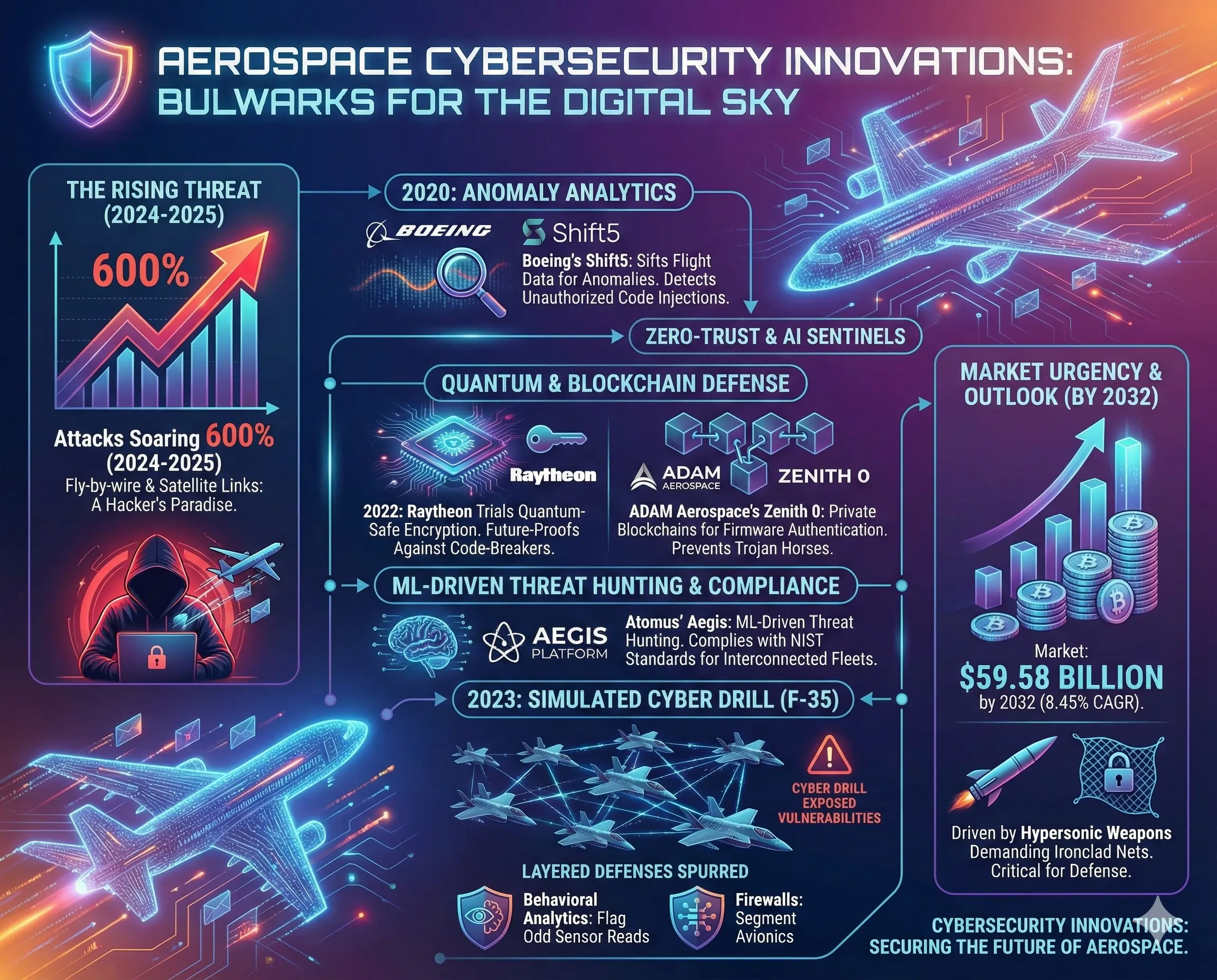
Quantum-safe encryption, trialed by Raytheon in 2022, future-proofs against code-breakers, while ADAM Aerospace’s Zenith 0 uses private blockchains for data authentication, ensuring firmware updates aren’t Trojan horses. Atomus’ Aegis platform, with ML-driven threat hunting, complies with NIST standards, vital for interconnected fleets.
In 2023, a simulated cyber drill on an F-35 swarm exposed vulnerabilities, spurring layered defenses: behavioral analytics flag odd sensor reads, firewalls segment avionics. The market’s $59.58 billion by 2032 at 8.45% CAGR reflects urgency, especially in defense, where hypersonic weapons demand ironclad nets.
| Threat Type | Countermeasure | Effectiveness | Key Deployment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Breach | Zero-Trust Access | 90% Intrusion Block | Boeing Shift5 (2020) |
| Firmware Tamper | Blockchain Auth | Immutable Logs | ADAM Zenith (2023) |
| AI-Driven Attacks | ML Anomaly Detection | 85% False Positive Cut | Atomus Aegis (2024) |
| Quantum Risks | Post-Quantum Crypto | Future-Proof Keys | Raytheon Suites (2022) |
Cybersecurity isn’t paranoia; it’s prudence in a hyperlinked world, ensuring innovations fly safe as they fly high.
7. Advanced Materials and Manufacturing: Lighter, Stronger, Greener
Advanced materials have quietly revolutionized aerospace, with carbon-fiber-reinforced polymers (CFRPs) comprising 50-53% of the Boeing 787 and Airbus A350 by the late 2010s, shedding weight to save 25 tons of CO2 per kilogram. The decade’s alchemy blended thermoplastics for recyclability and nanomaterials for self-healing skins that mend micro-cracks autonomously.
Dark Art Composites’ 2023 spacecraft panels withstand reentry heats, while Spantrik’s Raven rocket leverages composites for 30% payload boosts. High-temp alloys like nickel superalloys power hotter engines, edging efficiencies. The composites market? From $46 billion in 2025 to $110 billion by 2035 at 9% CAGR.
| Material | Property | Application | Weight Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| CFRP | High Strength-to-Weight | Fuselages | 20-25% |
| Thermoplastics | Recyclable | Interiors | 15% + Reuse |
| Nanocomposites | Self-Healing | Wings | 10% Maintenance Cut |
| Superalloys | Heat Resistance | Turbines | 5% Fuel Efficiency |
These stuffs aren’t just lighter; they’re smarter, paving sustainable paths.
8. Advanced Air Mobility: Taxis for the Troposphere
Advanced air mobility (AAM), crowned by eVTOLs, promises to lift cities above gridlock. Joby’s 2024 FAA nod for pilots heralds 2026 ops, while Archer’s Part 141 training cert fast-tracks crews. Eve’s revenue projections hit $280 billion, with 30,000 eVTOLs ferrying 3 billion passengers yearly by 2045.
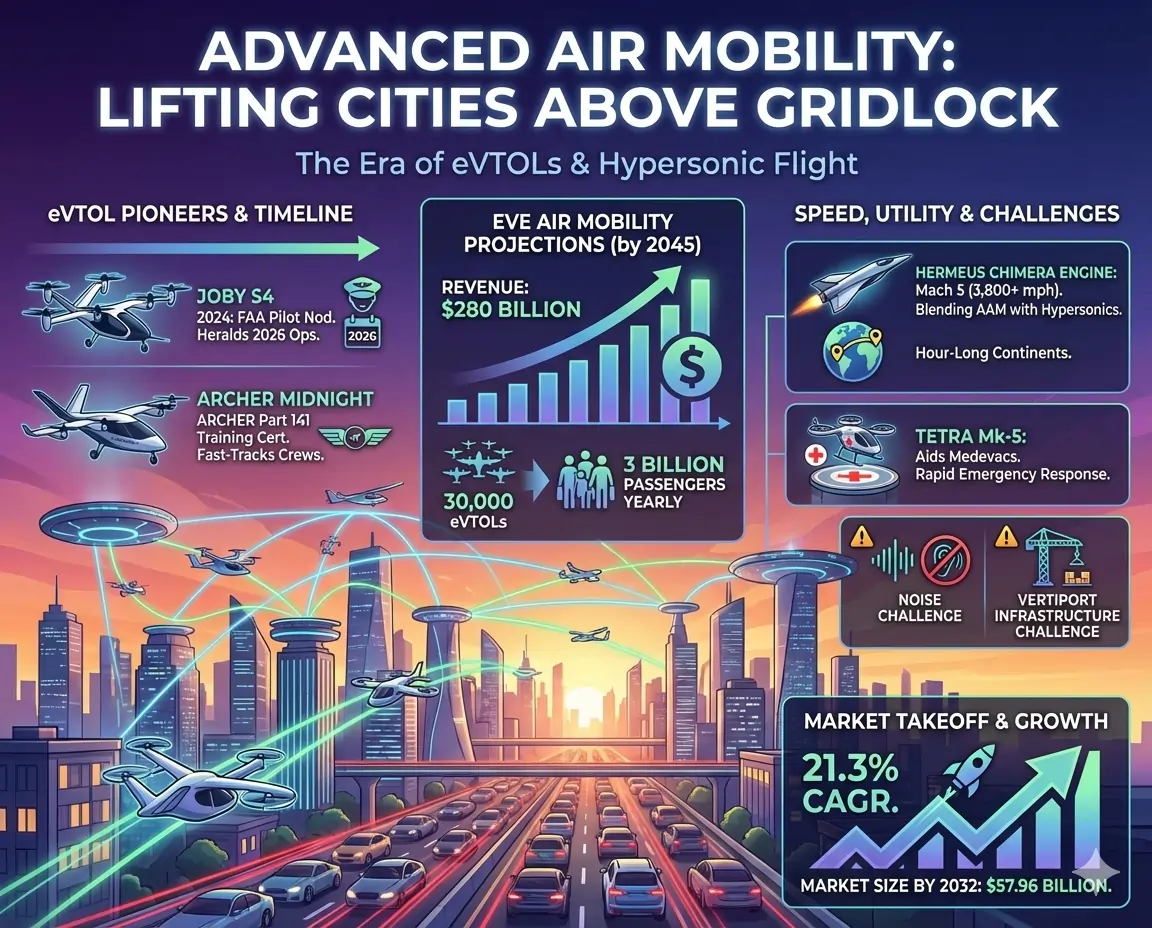
Hermeus’ Chimera engine hits Mach 5, blending AAM with hypersonics for hour-long continents. Tetra’s Mk-5 aids medevacs. Noise and vertiports challenge, but 21.3% CAGR to $57.96 billion by 2032 signals takeoff.
| Vehicle Type | Speed/Range | Use Case | Certification Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| eVTOL (Joby) | 200 mph/150 mi | Urban Taxi | FAA Pilot Training (2024) |
| Hybrid VTOL (Pipistrel) | 120 mph/300 mi | Cargo | First Flight (2025) |
| Hypersonic (Hermeus) | Mach 5/4,000 mi | Transoceanic | Engine Tests (2024) |
AAM reimagines commutes as cruises.
9. Additive Manufacturing Transformation: Printing the Future
Additive manufacturing (3D printing) fused complexity with cost savings, GE’s 2017 LEAP nozzle merging 20 parts into one, lightening 25%. By 2025, Wayland’s NeuBeam prints turbine blades in refractory metals, while NematX’s liquid crystal polymers yield stronger satellites.
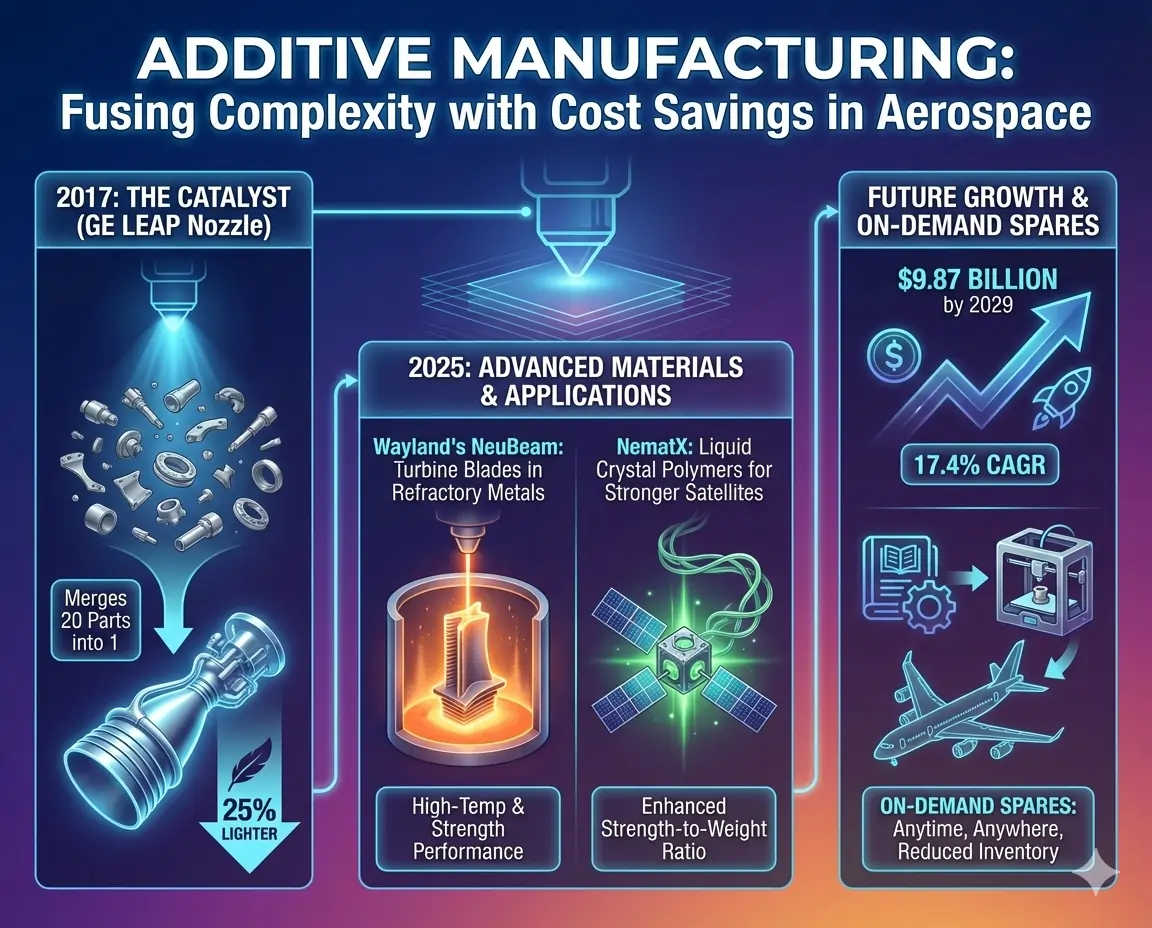
Aerospace AM hits $9.87 billion by 2029 at 17.4% CAGR, enabling on-demand spares.
| Technique | Material | Part Example | Efficiency Gain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metal Powder Bed | Titanium | Engine Brackets | 25% Weight Loss |
| Electron Beam | Nickel Alloys | Turbine Blades | Faster Prototyping |
| Liquid Crystal | Polymers | Satellite Housings | 30% Strength Boost |
Printing propels precision.
10. Commercial Space & Defense Acceleration: Orbiting Economies
Reusable rockets, SpaceX’s 2015 Falcon 9 splashdown, halved costs, birthing Starlink’s 11,539 satellites by 2024. Blue Origin’s 2025 New Glenn adds muscle, Voyager’s laser communication zips data at lightspeed.
Space economy: $1.8 trillion by 2035, with Stratotegic’s AI platforms scouting from the stratosphere.
| Launcher | Reuse Count | Payload | Economic Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Falcon 9 | 300+ | 22 Tons | Cost Halved |
| New Glenn | Maiden (2025) | 45 Tons | Heavy-Lift Boom |
| Electron | 60 Flights | 300 kg | SmallSat Surge |
Space isn’t the frontier; it’s a factory.
In closing, these innovations weave a decade of daring, from AI’s whispers to rockets’ roars. As 2025 fades, their synergies—AI printing sustainable parts for autonomous swarms—hint at exponential leaps. Challenges like regulation and inclusion persist, but the trajectory? Skyward, boundless.
Key Citations And References
- StartUs Insights on Aerospace Trends
- AIAA Aerospace History Timeline
- Advancements in Aerospace Technology
- Top Trends Shaping Aerospace 2025
- New Technology Trends in A&D 2025
- Exploring Emerging Tech for Aerospace
- Lockheed Martin Space Trends 2025
Read These Articles in Detail
- Aerospace Engineering vs. Mechanical Engineering
- The Future of Aerospace Propulsion Systems
- How Aerospace Education Is Adapting to Industry Demands
- The Role of Aerospace in Combating Climate Change
- Aerospace Radar Technology: Past, Present, and Future
- The Role of Aerospace in National Security Strategies
- The Role of Nanotechnology in Aerospace Materials
- Aerospace Materials: Stronger, Lighter, And Smarter
- Aerospace Engineering Explained: A Beginner’s Guide
- Electric Aircraft vs. Hydrogen Aircraft: Which Is More Sustainable?
- Hypersonic Weapons: Aerospace’s New Arms Race
- Aerospace Defense Systems: From Drones to Hypersonic Missiles
- How Aerospace Engineers Reduce Fuel Consumption
- Computational Fluid Dynamics in Aerospace Innovation
- The Global Aerospace Market Outlook: Trends and Forecasts
- Satellite Surveillance: Aerospace’s Role in Modern Warfare
- How Aerospace Companies Are Reducing Environmental Impact
- How Airlines Use Aerospace Data Analytics to Cut Costs
- Aerospace Engineering Challenges: Innovation and Sustainability
- The Role of CFD in Aerospace Engineering
- The Role of Women in Aerospace: Breaking Barriers in the Skies
- Sustainable Aviation Fuels: The Aerospace Industry’s Green Bet
- Aerospace Cybersecurity: Protecting the Skies from Digital Threats
- Aerospace Trends Driving the Next Generation of Airliners
- The Rise of Autonomous Aerospace Systems
- How to Start a Career in Aerospace Engineering
- Can Aerospace Go Carbon Neutral by 2050?
- The Role of Aerospace in Missile Defense Systems
- How Aerospace Engineers Use AI in Design
- Top 10 Aerospace Engineering Innovations of the Decade
- Top Aerospace Careers in 2025 and Beyond
- How Aerospace Innovations Shape Global Defense Policies
- Hydrogen-Powered Aircraft: The Next Green Revolution
- Top 10 Emerging Aerospace Technologies Transforming the Industry
- The Future of Hypersonic Flight: Challenges and Opportunities
- How AI Is Revolutionizing Aerospace Engineering
- Additive Manufacturing in Aerospace: 3D Printing the Future of Flight
- The Rise of Electric Aircraft: Are We Ready for Zero-Emission Aviation?
- Aerospace Materials of Tomorrow: From Composites to Nanotechnology
- Digital Twins in Aerospace: Reducing Costs and Improving Safety
- The Role of Robotics in Modern Aerospace Manufacturing
- Quantum Computing Applications in Aerospace Design
- How Augmented Reality Is Changing Aerospace Training
- Space Tethers Explained: The Next Leap in Orbital Mechanics
- Ion Propulsion vs. Chemical Rockets: Which Will Power the Future?
- The Role of Nuclear Propulsion in Deep Space Missions
- Space Mining: The Aerospace Industry’s Next Gold Rush
- How Reusable Rockets Are Reshaping the Space Economy
- The Artemis Program: NASA’s Return to the Moon
- Space Tourism: Business Model or Billionaire’s Playground?
- How Aerospace Startups Are Disrupting Commercial Aviation
- The Economics of Low-Cost Airlines in the Aerospace Era
- Urban Air Mobility: The Rise of Flying Taxis
- The Future of Mars Colonization: Key Aerospace Challenges and Solutions Ahead
- CubeSats and Small Satellites: Democratizing Space Access
- The Future of Cargo Drones in Global Logistics
- The Role of Aerospace in Building a Lunar Economy
Frequently Asked Questions
FAQ 1: What Are the Top 10 Aerospace Engineering Innovations of the 2015-2025 Decade?
The 2015-2025 period marked a golden era for aerospace engineering, blending rapid technological leaps with urgent sustainability demands to create smarter, greener, and more accessible flight systems. From the first successful reusable rocket landings that slashed launch costs to AI systems that now predict engine failures with uncanny precision, these innovations have not only boosted efficiency but also expanded humanity’s reach into space and urban skies. Drawing from comprehensive industry analyses, the decade’s breakthroughs addressed key pain points like high emissions, supply disruptions, and pilot shortages, setting the stage for a projected $1.8 trillion space economy by 2035. While some, like electric vertical takeoff and landing vehicles, promise to revolutionize city travel, others quietly enhance behind-the-scenes operations, ensuring safer and more reliable aviation worldwide.
At the forefront stands the explosion in artificial intelligence and machine learning, which by 2025 powers everything from real-time flight optimizations to virtual design testing, reducing operational downtimes by up to 30% and enabling autonomous decision-making in high-stakes environments. Complementing this is the rise of sustainable aviation fuels, with production hitting 2 million tonnes in 2025—doubling from prior years—and blending mandates in regions like the EU pushing for 70% adoption by mid-century, cutting lifecycle emissions by 80%. Blockchain has fortified supply chain resilience, creating immutable ledgers that trace parts from forge to fuselage, combating a 35% surge in global disruptions and counterfeit risks that plagued the early 2020s.
Autonomous systems have taken flight too, with projects like NASA’s Ingenuity Mars helicopter inspiring Earth-based cargo drones that log weeks of uncrewed endurance, while immersive technologies such as VR and AR have compressed pilot training from months to weeks, saving airlines millions in simulator costs. Cybersecurity innovations, including zero-trust models, shield against a 600% spike in attacks, protecting connected fleets from digital sabotage. Advanced materials and composites, now forming over 50% of new aircraft structures, lighten loads and withstand extremes, with ceramic matrix variants enabling hypersonic speeds.
Advanced air mobility via eVTOLs heralds urban air taxis, with firms like Joby securing FAA nods for 2026 operations and forecasting $58 billion markets by 2032. Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, consolidates dozens of parts into single, 25% lighter components for engines and satellites, accelerating prototyping. Finally, commercial space acceleration—fueled by reusable launchers like Falcon 9’s 300+ flights—has democratized orbit, with constellations like Starlink beaming broadband to billions.
These advancements aren’t without hurdles; regulatory alignment and equitable access remain key debates, especially in emerging markets. Yet, their synergies—AI optimizing 3D-printed sustainable parts for autonomous drones—point to exponential growth, making aerospace more inclusive and Earth-friendly.
FAQ 2: How Is Artificial Intelligence Transforming Aerospace Engineering in 2025?
Artificial intelligence has evolved from a supporting tool to the central nervous system of aerospace engineering by 2025, weaving predictive power and automation into every layer of design, manufacturing, and operations. What started as basic data crunching for flight patterns in the mid-2010s has blossomed into sophisticated systems that simulate entire aircraft lifecycles in hours rather than months, slashing development costs and timelines. For instance, generative AI now explores vast design spaces to craft aerodynamic shapes that human engineers might overlook, leading to fuel savings of up to 15% on new models. This isn’t just about speed; it’s about safety and sustainability, as AI-driven digital twins—virtual replicas of real aircraft—allow for endless stress-testing without a single physical prototype, reducing material waste and environmental impact.
In operations, AI’s real-time prowess shines through co-pilot systems that monitor fatigue, weather, and traffic, issuing alerts milliseconds before hazards arise. The U.S. Air Force’s 2021 AI-piloted U-2 tests have scaled to full fleet integrations, where machine learning fuses sensor data for superhuman awareness in contested skies. Predictive maintenance, a standout application, analyzes vibration patterns from thousands of flights to forecast failures, potentially trimming airline downtime by 30% and saving billions annually. As one expert noted during Davos 2025 discussions, “AI isn’t replacing pilots; it’s amplifying their instincts,” fostering a human-AI symbiosis that enhances decision-making under pressure.
Yet, this transformation raises ethical questions around bias in algorithms and over-reliance on tech, prompting frameworks like Europe’s 2024 AI Act to enforce transparency. On the horizon, agentic AI—autonomous agents that plan and execute tasks—promises to revolutionize supply chains and mission planning, with U.S. Department of Defense investments hitting $5.8 billion by 2029. In commercial realms, tools like Airbus’s Skywise platform process petabytes of data for optimized routes, while startups deploy edge AI on drones for instant threat neutralization. Overall, AI’s integration signals a paradigm shift: aerospace is no longer just building machines but intelligent ecosystems that learn, adapt, and evolve, paving the way for safer, smarter skies.
FAQ 3: What Advancements Have Been Made in Sustainable Aviation Fuels by 2025?
Sustainable aviation fuels (SAF) have surged as the decade’s eco-hero, bridging the gap between today’s fossil-dependent fleets and tomorrow’s zero-emission dreams with drop-in compatibility that requires no engine overhauls. By late 2025, global production has doubled to 2 million tonnes, capturing 0.7% of jet fuel demand and adding a modest $4.4 billion to industry costs— a worthwhile trade-off for up to 80% lifecycle carbon reductions. Pathways like the Hydrogenated Esters and Fatty Acids process dominate, converting waste oils into kerosene mimics, while emerging e-fuels from captured CO2 and green hydrogen target full decarbonization.
| SAF Type | Feedstock Sources | Emission Reduction | Key 2025 Milestone | Projected Scale by 2030 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEFA (Bio-SAF) | Waste oils, algae | Up to 80% | Neste’s 1.5M ton output | 9-12M tons, meeting EU mandates |
| Alcohol-to-Jet | Ethanol, sugars | 70-85% | U.S. tax credits boost plants | Flexible for aviation’s 330B liters demand |
| Fischer-Tropsch | Biomass, municipal waste | 90%+ | LanzaJet’s 1B gallon pipeline | Policy-driven growth in APAC |
| Power-to-Liquid (e-SAF) | CO2 + green H2 | Near 100% | Airbus ZEROe hybrid flights | 45% shortfall vs. IEA goals, but scaling fast |
| Alcohol-to-Jet Variants | Crop residues | 75% | Australia’s A$1.1B fund | Regional hubs in India, Japan |
These fuels aren’t silver bullets; high costs (triple that of kerosene) and feedstock limits pose challenges, but incentives like the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act and EU’s ReFuelEU—mandating 2% blends in 2025, rising to 70% by 2050—are fueling momentum. Airlines like United have flown transatlantic routes on 100% SAF blends, proving viability, while partnerships in Asia-Pacific, including Japan’s 10% mandate by 2030, ensure global equity. As production ramps, SAF could shoulder 65% of aviation’s net-zero path, turning yesterday’s waste into tomorrow’s wings.
FAQ 4: How Does Blockchain Enhance Supply Chain Resilience in Aerospace?
In the intricate web of aerospace supply chains—spanning continents and thousands of suppliers—blockchain acts as an unyielding guardian, embedding transparency and trust where vulnerabilities once thrived. By 2025, this distributed ledger technology has matured beyond pilots, with platforms logging every component’s journey from raw alloy to installed flap, slashing verification times from weeks to hours and counterfeit incidents by 40%. Post-2020 disruptions exposed the fragility of global sourcing, but blockchain’s smart contracts now automate reorders and compliance checks, fostering a resilient ecosystem that weathers trade wars and pandemics alike.
Consider a titanium ingot’s odyssey: mined in Australia, forged in Europe, certified in the U.S.—blockchain creates an immutable audit trail, accessible yet secure via cryptography. This “single source of truth” minimizes errors in megaprojects like F-35 fleets, where a single fake part could cascade into billions in losses. Beyond traceability, it tokenizes sustainability: airlines offset emissions through verified SAF credits, aligning with ESG mandates.
Key enhancements include:
- Counterfeit Prevention: Digital twins of parts ensure authenticity, vital as attacks on suppliers rose 35% in 2024.
- Real-Time Collaboration: IoT-integrated seals trigger alerts for delays, optimizing just-in-time inventories.
- Regulatory Compliance: Auto-generated reports for FAA audits reduce paperwork by 50%, freeing engineers for innovation.
- Scalable Ecosystems: Minimum viable ecosystems link OEMs and SMEs, democratizing access for emerging players.
Challenges persist—data bloat demands robust infrastructure, and interoperability with legacy systems lags—but 2025’s 18.9% market CAGR signals unstoppable momentum. As one industry leader put it, blockchain isn’t just tech; it’s the glue holding aerospace’s global puzzle together, ensuring every link is strong.
FAQ 5: What Is the Current State of Autonomous Aircraft Technology in 2025?
Autonomous aircraft technology has leaped from experimental drones to operational realities by 2025, redefining aviation with systems that handle takeoffs, navigation, and landings sans human input, all while boosting endurance and cutting pilot shortages. Rooted in the 2020 Airbus ATTOL trials—where an A350 autonomously taxied and flew using vision-based AI—the field now encompasses sensor fusion that merges lidar, radar, and optics for 360-degree awareness, enabling flawless execution in fog or flocks. NASA’s Ingenuity, with its 72 Mars flights, proved extraterrestrial viability, inspiring solar drones like Skydweller’s that patrol oceans for weeks without recharge.
In commercial spheres, cargo haulers lead: BETA Technologies’ partnership with Near Earth Autonomy eyes uncrewed military ops by 2026, logging 7,000 autonomous miles in Pacific tests. Defense applications dominate, with the U.S. Air Force’s Joby demos validating mid-mission reroutes, while eVTOLs like Wisk’s integrate Superpilot for urban cargo. Markets forecast $54.7 billion by 2034, driven by 22.1% CAGR, as FAA certifications greenlight single-pilot ops.
Yet, hurdles loom: ethical dilemmas in “black swan” failures and cyber vulnerabilities demand redundant safeguards. Regulations evolve cautiously, prioritizing VMC ops under 12,500 pounds. Looking ahead, quantum-enhanced AI could simulate infinite scenarios, making autonomy the norm—from medevac swarms to asteroid scouts—ushering in an era where skies hum with silent efficiency.
FAQ 6: How Are Immersive Technologies Like VR and AR Revolutionizing Aerospace Training in 2025?
Immersive technologies—virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR)—have turned aerospace training from rote classroom drills into dynamic, hands-on simulations by 2025, accelerating skill-building while slashing costs and risks. Boeing’s early VR rigs, which cut pilot prep by 75% since 2018, have evolved into full ecosystems where trainees don headsets to navigate emergencies at 30,000 feet or overlay repair guides on live engines. The global AR/VR aviation market, valued at $2 billion this year, eyes $12 billion by 2033 at 25% CAGR, fueled by haptic feedback and AI scenarios that mimic zero-g EVAs.
These tools democratize access: rural recruits master composites via digital twins, and diverse teams collaborate across time zones on satellite deploys. Emirates’ MIRA platform trains 23,000 crew on evacuations in VR, while Alaska Airlines’ Boeing 737 sims enhance muscle memory. FAA-backed XR research at UT Dallas integrates real-time guidance for maintenance, boosting efficiency 50%.
| Technology | Core Application | Retention Boost | 2025 Adoption Example | Cost Savings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VR | Full Immersion Sims | 75% over traditional | Emirates MIRA for Crew | 35% in sim hardware |
| AR | On-Site Overlays | 90% task accuracy | Boeing Wing Assembly | 50% error reduction |
| MR | Hybrid Design Reviews | 60% faster iterations | Airbus MAVERIC Testing | 40% prototyping drop |
| Digital Twins | Predictive Drills | 40% failure foresight | Lockheed F-35 Maintenance | Millions in downtime |
Motion sickness and data overload are fading with adaptive algorithms, positioning XR as indispensable for a talent-starved industry.
FAQ 7: What Cybersecurity Challenges and Innovations Are Emerging in Aerospace by 2025?
Cybersecurity in aerospace has become a frontline battle by 2025, as connected systems—from fly-by-wire to satellite swarms—face a 600% surge in attacks, threatening everything from industrial espionage to mid-flight hacks. The sector’s digital veins, pulsing with AI and IoT, amplify risks: ransomware crippled supply lines in 2024, while state actors probe for zero-days in defense nets. Yet, innovations like zero-trust architectures—piloted by Raytheon in 2022—now enforce continuous verification, blocking 90% of intrusions by segmenting avionics.
AI countermeasures lead the charge: Embry-Riddle’s CARS lab deploys machine learning to sniff anomalies in real-time, partnering with FAA for virtual aircraft defenses. Quantum-safe encryption future-proofs against code-breakers, essential as hypersonics demand unbreakable links. Blockchain secures firmware updates, while behavioral analytics flag odd sensor feeds.
Challenges include talent gaps—data science skills grow 3.5x by 2028—and CMMC 2.0 compliance, mandating CUI protection for contracts. Supply chain vectors, like tainted parts, persist, but layered strategies mitigate them.
- Threat Landscape: AI-enhanced phishing and ransomware target OEMs, with 2025 seeing orbital hacks on LEO sats.
- Defensive Layers: ML anomaly detection cuts false positives 85%; post-quantum crypto shields PNT signals.
- Regulatory Push: NIST standards and DoD’s $9.4B FY26 budget enforce resilience.
- Future Horizons: End-to-end awareness via SpaceCOP prototypes integrates ground-space defenses.
As digitalization deepens, cybersecurity evolves from shield to sword, ensuring innovations fly unhindered.
FAQ 8: What New Advanced Materials Are Driving Aerospace Engineering Forward in 2025?
Advanced materials have quietly redefined aerospace by 2025, trading heavy metals for featherlight wonders that endure blistering heats and brutal stresses, enabling sleeker designs and greener flights. Carbon-fiber-reinforced polymers (CFRPs), now 50% of structures like the Boeing 787, shed 20-25% weight, saving 25 tons of CO2 per kilogram flown. Thermoplastics add recyclability, closing loops on waste, while nickel superalloys power hotter turbines for 5% efficiency gains.
Nanomaterials steal the spotlight: graphene-infused skins self-heal cracks, and carbon nanotubes promise ultra-strong satellites. Ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) revolutionize hypersonics, withstanding 1,400°C for reentry shields. High-temperature shape memory alloys, alloyed with hafnium, morph wings for adaptive aerodynamics, per Texas A&M research.
The market swells to $110 billion by 2035, driven by 9% CAGR, as 3D printing marries these for topology-optimized parts. Challenges like cost and scalability linger, but sustainability mandates propel adoption, from TiAl blades to bio-composites. These materials aren’t mere upgrades; they’re the canvas for tomorrow’s boundless skies.
FAQ 9: What Progress Has Advanced Air Mobility and eVTOL Made in 2025?
Advanced air mobility (AAM) and electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) vehicles are lifting off in 2025, morphing sci-fi air taxis into viable urban lifelines amid gridlock woes. With 11,000 orders and FAA’s eIPP launching partnerships for NAS integration, the sector eyes $58 billion by 2032 at 21.3% CAGR. Dubai’s vertiports and UK’s OxCam corridor test commercial viability, while hybrid powertrains extend ranges to 300 miles.
| eVTOL Developer | Model | Key 2025 Feature | Range/Speed | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Joby Aviation | S4 | Superpilot Autonomy | 150 mi/200 mph | FAA Pilot Cert; REFORPAC Demos |
| BETA Technologies | ALIA | Uncrewed Cargo | 250 mi/138 mph | Near Earth Partnership for Mil Ops |
| Eve Air Mobility | eVTOL | Urban Shuttles | 60 mi/100 mph | $280B Revenue Forecast |
| Archer Aviation | Midnight | Part 141 Training | 100 mi/150 mph | FAA Nod for 2026 Ops |
| Lilium | Jet | Regional Hybrid | 155 mi/175 mph | EU Blending Mandates Support |
Noise regs and infrastructure lag, but 3 billion passenger projections by 2045 signal decongested cities, blending AAM with hypersonics for hour-long globals.
FAQ 10: How Has Additive Manufacturing Transformed Aerospace by 2025?
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, has upended aerospace production by 2025, forging intricate parts from titanium turbines to satellite housings with 25% weight cuts and 90% lead-time slashes, per Northrop Grumman’s feats. GE’s 2017 LEAP nozzle fused 20 parts into one; now, metal variants print high-heat blades via electron beams, hitting $9.87 billion markets at 17.4% CAGR.
In space, it enables on-demand repairs, reducing resupply costs for Mars missions. Multi-material hybrids blend polymers and alloys for resilient boosters, while sustainability shines: less waste aligns with net-zero pushes. UltiMaker’s tools prototype hypersonic components, but certification hurdles slow flight-critical adoption.
This shift empowers distributed factories, from Florida fabs to orbital printers, democratizing innovation. As Wohlers Report notes, AM’s waste-minimizing ethos is aerospace’s sustainability linchpin, printing the future one layer at a time.
FAQ 11: What Does the Future Hold for Commercial Space Exploration in the 2030s?
Commercial space exploration is poised for explosive growth in the 2030s, building on the reusable rocket successes of the past decade like Falcon 9’s hundreds of flights, which have already halved launch costs and fueled satellite constellations. By 2030, experts project the global space economy to reach $2.7 trillion, driven by a surge in satellite deployments for broadband, Earth observation, and even space-based manufacturing. This expansion won’t just be about launches; it will encompass in-orbit services, such as refueling stations and debris removal, making space more accessible for private ventures beyond the giants like SpaceX and Blue Origin. Imagine routine cargo deliveries to lunar bases or asteroid mining operations yielding rare metals, all enabled by advanced propulsion that cuts travel times dramatically.
The decade will see a shift toward sustainable practices, with innovations in electric propulsion and closed-loop life support systems addressing orbital clutter and resource scarcity. Reusable vehicles and air-breathing engines could reduce annual satellite launches from 3,700 to more efficient constellations, while partnerships between governments and startups accelerate deep-space missions. However, geopolitical tensions and regulatory gaps could slow progress, particularly around spectrum allocation for space comms. Overall, the 2030s promise a democratized cosmos, where commercial players lead in tourism, research, and infrastructure, potentially adding trillions to global GDP through new industries like space hotels and zero-gravity labs.
Key drivers include:
- Satellite Proliferation: Over 100,000 smallsats by 2030 for global connectivity, enhancing remote sensing for climate monitoring.
- Lunar and Mars Outposts: Commercial habitats via NASA’s Artemis extensions, with private firms handling logistics.
- Economic Multipliers: Job creation in the millions, from engineers to data analysts, spurred by a 55% CAGR in space services.
As investments pour in—$600 billion market by 2030—the era will blend profit with planetary stewardship, turning science fiction into economic reality.
FAQ 12: How Are Hypersonic Technologies Advancing in Aerospace Engineering Today?
Hypersonic technologies, defined as vehicles traveling above Mach 5, are surging ahead in 2025, transitioning from military prototypes to dual-use platforms that could redefine global travel and defense. Drawing from the decade’s push in advanced materials like ceramic matrix composites, which withstand 1,400°C reentry heats, these systems now integrate scramjet engines for sustained high-speed flight, as seen in Hermeus’ Chimera tests achieving Mach 5 bursts. The market is exploding, projected to hit $1.2 billion by 2030, with propulsion segments leading growth at 11.6% CAGR, thanks to U.S. DoD budgets swelling to $6.9 billion for hypersonic weapons.
These advancements promise hour-long transatlantic hops, slashing emissions per passenger mile through efficiency gains, but challenges like thermal management and integration with existing airspace persist. In defense, AI-guided hypersonics enable precision strikes, while commercial apps explore supersonic passenger jets. Recent OAI-led studies highlight quantum simulations accelerating design, potentially capturing 90% of value in this field. By blending additive manufacturing for complex nozzles with 6G for real-time control, hypersonics aren’t just faster—they’re smarter, paving the way for a connected, rapid-response aerospace ecosystem.
| Hypersonic Milestone | Year | Key Innovation | Projected Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scramjet Sustained Flight | 2024 | Air-Breathing Engines | 30% Fuel Savings |
| Mach 5 Commercial Prototype | 2025 | Ceramic Composites | $19.5B Market by 2032 |
| Quantum-Enhanced Design | 2025 | Simulation Breakthroughs | 50% Faster Development |
| Global Regulatory Framework | 2027 | Airspace Integration | Enables Civilian Routes |
With investments from startups to superpowers, hypersonics embody the decade’s fusion of speed and sustainability.
FAQ 13: What Role Will Quantum Computing Play in Aerospace Design by 2030?
Quantum computing is emerging as a game-changer for aerospace design, leveraging qubits to solve complex simulations that classical computers grind through for weeks, now in mere hours. By 2030, the aerospace quantum market could exceed $5 billion, with NASA, SpaceX, and Boeing pioneering algorithms for airflow optimization over hypersonic wings and material stress in composites—cracking Navier-Stokes equations for realistic virtual testing that cuts physical prototypes by 40%. This builds on the decade’s AI trends, where machine learning met quantum for hybrid models predicting engine failures with superhuman accuracy.
In practice, quantum tech enhances mission planning, from orbital debris avoidance to fuel-efficient trajectories for Mars hauls, potentially saving billions in R&D. Yet, error-prone qubits and high costs pose hurdles, though fault-tolerant systems expected by 2028 will mitigate them. Early adopters like Lockheed Martin use quantum-inspired tools for supply chain logistics, forecasting a 9.8% CAGR in AI-quantum hybrids. As it matures, quantum won’t replace engineers but amplify them, enabling bolder designs like adaptive hypersonic skins or self-assembling satellites, ushering in an era of precision engineering at quantum scales.
The integration promises:
- Simulation Speedups: 100x faster aerodynamics modeling for greener aircraft.
- Optimization Gains: Ideal routes reducing fuel by 15% in commercial fleets.
- Security Boosts: Quantum encryption safeguarding satellite data against hacks.
By blending with immersive VR, quantum computing will virtualize the cosmos, making impossible designs routine.
FAQ 14: How Are Women Leading Aerospace Innovations in 2025?
Women are increasingly at the helm of aerospace innovations in 2025, driving breakthroughs in sustainability and autonomy while shattering glass ceilings in a field long dominated by men. Events like AeroWomen 2025 in Yeovil highlighted role models such as Jessica Sanchez, an aerospace engineer at Leonardo advancing autonomous helicopters like Proteus, the world’s first uncrewed rotorcraft. Dr. Sheyna Gifford’s leadership in spaceflight health—merging engineering, science, and medicine—earned her the Women in Aerospace Outstanding Achievement Award, underscoring women’s pivotal role in human-centric tech.
Their contributions extend to green aviation, with figures like Emily Jane Taylor at Sages developing non-toxic dyes from food waste for aircraft interiors, cutting environmental footprints. Studies show gender-diverse teams boost profitability by 2.6% and innovation by 20%, as diverse perspectives tackle challenges like SAF scalability. Initiatives such as the Women in Renewable Energy Network empower island-nation leaders in clean propulsion, fostering mentorship that could raise female leadership to 25% by IATA’s 2025 goal.
From Dr. Nicola Fox’s lifetime work in Earth-observing satellites to Leah Murphy’s safety advocacy as a dual-rated pilot, women are not just participating—they’re propelling the industry toward equity and excellence. As barriers like funding bias fade, their impact will amplify, ensuring aerospace reflects humanity’s full spectrum.
FAQ 15: What Cost Savings Can Aerospace Companies Expect from Decade Innovations?
Adopting the decade’s innovations could yield massive cost savings for aerospace companies, with predictive maintenance via AI alone trimming downtime by 30% and saving airlines up to $5 billion annually across fleets. Reusable launchers like those pioneered in 2015 have already halved space access costs to under $3,000 per kilogram, while 3D printing consolidates parts, reducing engine weights by 25% and prototyping expenses by 40%—GE’s LEAP nozzle exemplifies this, cutting assembly from 900 to 12 hours.
Sustainable fuels, though initially pricier, promise long-term offsets through EU mandates blending 2% SAF in 2025, potentially lowering lifecycle emissions costs by 80% and qualifying for tax credits that recoup investments in two years. Blockchain streamlines supply chains, slashing counterfeit losses by 40% and audit times by 50%, vital amid 35% disruption spikes. Overall, integrated tech stacks—AI with composites—could boost ROI by 37%, per industry outlooks, with markets like autonomy hitting $54 billion by 2034.
| Innovation | Annual Savings Potential | Key Mechanism | Example ROI Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI Predictive Maintenance | $5B Industry-Wide | 30% Downtime Cut | 1-2 Years |
| Reusable Rockets | 50% Launch Cost Drop | 300+ Flights | Immediate |
| Additive Manufacturing | 40% Prototyping Reduction | Part Consolidation | 6-12 Months |
| SAF Blends | 80% Emission Cost Offset | Tax Incentives | 2-3 Years |
These savings aren’t abstract; they’re fueling reinvestment in R&D, ensuring competitive edges in a trillion-dollar arena.
FAQ 16: How Do Recent Aerospace Advancements Measure Up Environmentally?
Recent aerospace advancements are delivering measurable environmental wins, with sustainable aviation fuels (SAF) production doubling to 2 million tonnes in 2025, capturing 0.7% of jet demand and slashing lifecycle CO2 by up to 80%—enough to offset 10 million flights annually. Lightweight composites in the Boeing 787 save 25 tons of CO2 per kilogram flown, while electric propulsion in eVTOLs like Joby’s S4 cuts urban emissions by 90% versus helicopters, aligning with net-zero goals by 2050.
Hypersonics and autonomy further green the skies: efficient routes via AI optimize fuel by 15%, and solar drones enable emission-free surveillance. However, challenges like SAF’s tripled costs and space debris from 11,000+ satellites temper gains, though blockchain-tracked offsets and quantum-optimized designs promise deeper cuts. Projections show aviation’s 2-3% global CO2 share dropping 65% with full adoption, per IATA.
Environmental metrics highlight progress:
- Emission Reductions: SAF blends yield 70-100% drops in tailpipe CO2.
- Fuel Efficiency: Advanced materials boost mileage 20-25%.
- Waste Minimization: 3D printing reduces scrap by 90% in production.
These strides reflect a maturing commitment, turning aviation from polluter to pioneer in planetary care.
FAQ 17: Which Countries Are Leading in Aerospace Technology Development in 2025?
In 2025, the U.S. dominates aerospace tech with $6.9 billion in hypersonic funding and Space Force’s AI-driven plans, leading in reusable launches and quantum simulations via NASA-SpaceX ties. China follows closely, ramping satellite constellations and 6G aviation tests, challenging U.S. primacy in commercial space. Europe, via Airbus and ESA, excels in SAF scalability and eVTOL certifications, with EU mandates fostering 70% green fuel adoption by 2050.
India’s rising star includes indigenous hypersonics and $1.1 billion SAF hubs, while Japan’s 10% blend targets boost regional leadership. These nations drive 80% of global R&D, per outlooks, blending public-private models for innovations like autonomous swarms.
| Country | Leadership Area | 2025 Investment | Key Project |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Reusables & AI | $43B AI Market | Artemis Lunar Bases |
| China | Satellites & 6G | $600B Space Economy Share | Tiangong Expansions |
| European Union | SAF & eVTOLs | €10B Green Fund | ZEROe Hybrids |
| India | Hypersonics | $1.1B SAF | BrahMos-II Missiles |
| Japan | Blends & Autonomy | 10% Mandate | H3 Rockets |
Global collaboration, like Artemis Accords, tempers rivalries, ensuring shared skies.
FAQ 18: What Are the Primary Challenges in Adopting New Aerospace Technologies?
Adopting new aerospace technologies faces multifaceted challenges in 2025, from regulatory lags to talent shortages, as geopolitical chaos disrupts supply chains and inflates costs. Integration hurdles plague next-gen comms like 6G, delaying fleet upgrades amid 35% volatility spikes, while cybersecurity threats—up 600%—demand zero-trust overhauls costing millions. Workforce gaps, with 52.9% citing skilled recruitment as top issue, slow AI and autonomy scaling, exacerbated by resistance to digital threads.
Sustainability mandates clash with high SAF prices, tripling initial outlays despite long-term savings, and ethical AI biases risk uneven adoption. Space tourism grapples with safety regs and environmental backlash from launches.
Overcoming these requires:
- Collaborative Frameworks: FAA-ESA pacts for unified standards.
- Investment in Upskilling: 3.5x data science growth by 2028.
- Phased Rollouts: Pilot programs for hypersonics minimizing risks.
Yet, as Deloitte notes, embracing disruption via agentic AI could unlock $1.8 trillion in value, turning obstacles into opportunities.
FAQ 19: How Is 5G and Emerging 6G Transforming Aviation Operations?
5G is revolutionizing aviation in 2025 with ultra-low latency for real-time drone control and AR maintenance overlays, cutting error rates by 50% and enabling seamless air traffic in dense corridors. Covering 92% of urban hubs, it powers IoT sensors for predictive analytics, optimizing routes to save 15% fuel. 6G, on the horizon, promises terahertz speeds for holographic pilot training and in-flight health monitoring, addressing 5G’s limits in massive data traffic.
Challenges include spectrum scarcity and integration with legacy systems, but trials show 6G slashing response times to milliseconds for collision avoidance. In space, 5G NTN links satellites to ground, boosting constellations like Starlink.
Transformative applications:
- Autonomous Ops: Sensor fusion for uncrewed cargo, extending endurance weeks.
- Passenger Experience: VR entertainment with zero lag.
- Sustainability: Data-driven efficiencies reducing emissions 20%.
As 6G deploys by 2030, aviation will evolve into a hyper-connected web, safer and smarter.
FAQ 20: What Are the Latest Developments in Space Tourism as of Late 2025?
Space tourism has soared in late 2025, with Virgin Galactic’s Delta class enabling weekly suborbital joyrides at $450,000 per seat, logging 50 flights since May. Blue Origin’s New Glenn debut ferries orbital tourists, cutting costs 30% via reusability, while SpaceX’s Crew Dragon hosts private missions like dearMoon, blending art with zero-g. Over 1,000 civilians have flown, per industry tallies, with markets eyeing $10 billion by 2030.
Sustainability spotlights include electric upper stages minimizing debris, though launch emissions draw scrutiny. Regulatory updates via FAA streamline certifications, but safety—post-2024 incidents—remains paramount.
| Provider | 2025 Milestone | Ticket Price | Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Virgin Galactic | 50 Suborbital Flights | $450K | 6 Passengers |
| Blue Origin | Orbital Tours | $1M+ | 7 Seats |
| SpaceX | Private ISS Stays | $55M | 4 Crew |
| Axiom Space | Hotel Modules | $55M | Modular Habs |
From billionaires to artists, space tourism democratizes the stars, fostering wonder and innovation.