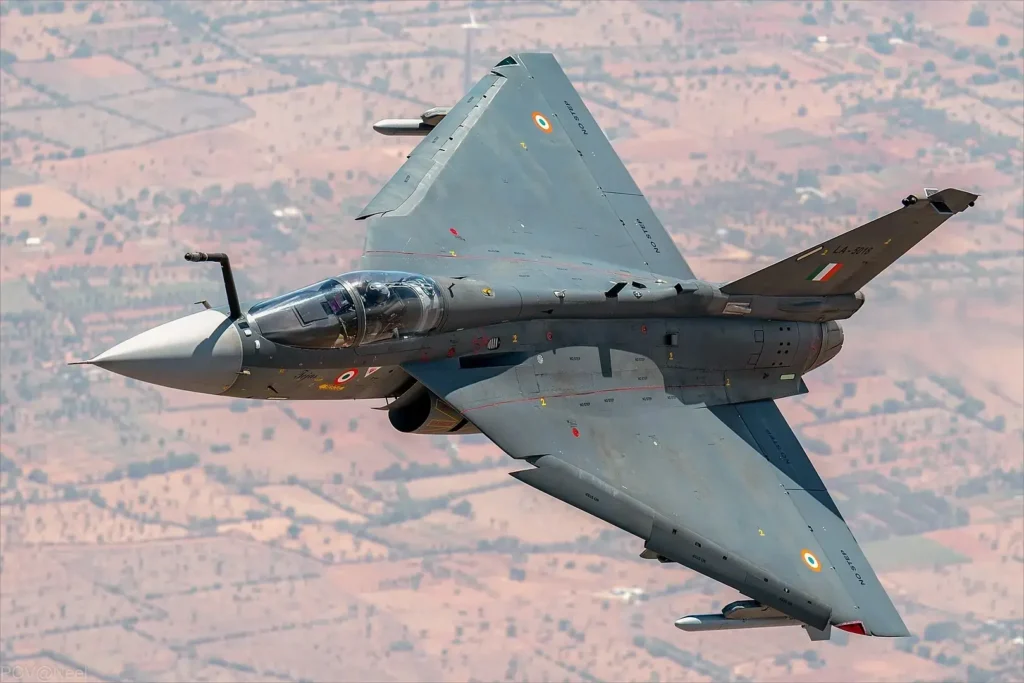
The Tejas, a single-seat, single-engine, lightweight, high-agility supersonic fighter aircraft, was introduced into the Indian Air Force (IAF) in July 2016. This remarkable aircraft, built by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), has quickly made its mark in the Indian military. Let’s delve into the detailed journey, specifications, and features of this indigenous marvel.
Table of Contents
Tejas Light Combat Supersonic Fighter Specifications
| Specifications: | Details: |
|---|---|
| Aircraft Name | Tejas |
| Type | Single-seat, single-engine, lightweight, high-agility supersonic fighter aircraft |
| Manufacturer | Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) |
| Entered Service | July 2016 |
| Design and Development | Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) |
| Prime Industrial Contractor | Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) |
| Test Flights | 4,599 (Up to speeds of Mach 1.4) |
| Carrier Variant | Approved in 1999 |
| Maiden Flight (Demonstrator I) | January 2001 |
| Maiden Flight (Demonstrator II) | June 2002 |
| Maiden Flight (PV-II) | December 2005 |
| Maiden Flight (Third Prototype) | December 2006 |
| Limited Series Production Approved | April 2006 |
| First Production Aircraft Maiden Flight | April 2007 |
| First Tejas Trainer Variation Maiden Flight | November 2009 |
| Initial Operational Clearance (IOC) | December 2010 |
| Certification Approved | January 2011 |
| Maiden Flight (LSP-7) | March 2012 |
| Maiden Flight (LSP-8) | March 2013 |
| Infrared-seeking Air-to-Air Missile Test | December 2013 |
| Initial Operational Clearance (IOC) Achieved | December 2013 |
| First Prototype with Advanced EW Suite Maiden Flight | October 2014 |
| First Series Production Aircraft Maiden Flight | October 2014 |
| Handover to Indian Air Force | January 2015 |
| Second Series Production Aircraft Maiden Flight | March 2016 |
| Naval Prototype Maiden Flight | April 2012 |
| Handover to Indian Air Force | July 2016 |
| Delta Platform Design | Approved in 1999 |
| Lightweight Materials Used | Aluminum, lithium, titanium alloys, carbon composites |
| Cockpit Features | Night vision compatible glass cockpit, Martin Baker zero-zero ejection seats |
| Multifunction Displays | Two 76mm × 76mm color liquid crystal multifunction displays |
| Head-up Display | Developed by the Central Scientific Instruments Organisation (CSIO) |
| Helmet-mounted Display and Sight (HMDS) | Included |
| Fly-by-wire System | Quadruplex digital automatic flight control |
| Navigation Suite | Sagem SIGMA 95N ring laser gyroscope inertial navigation system |
| Communications Suite | VHF to UHF radio communications, air-to-air and air-to-ground data link |
| Avionics Suite | Integrated utility health-monitoring system, ground proximity warning system |
| Terrain-referenced navigation system, instrument landing system, global positioning system, stores management system, three 1553B 32-bit mission computers | |
| Weapons Hardpoints | Eight external hardpoints |
| Gun | 23mm twin-barrelled GSh-23 gun installed in a blister fairing under the intake |
| Missiles | R-73 air-to-air missile, Derby BVR-AAM missile |
| Electronic Warfare Suite | Radar warning receiver and jammer, laser warner, missile approach warner, chaff and flare dispenser |
| Radar | Multimode radar with multiple target search track-while-scan and ground-mapping modes |
| Sensor Package (Mk1A variant) | Offered by Saab, includes AESA fighter radar technology and an EW suite |
| Engine (Prototype) | General Electric F404-GE-F2J3 turbofan engines with afterburn |
| Engine (Production) | General Electric 85kN F404-GE-IN20 turbofan engine with full authority digital engine control |
| New Engine (Prototype) | GTX-35VS Kaveri developed by Gas Turbine Research Establishment (in development) |
| Maximum Speed | 2,205 km/h |
| Maximum Altitude | 15,200 m |
| Range | 3,000 km |
| Service Ceiling | 16,500 m |
| Weight | Approximately 5,450 kg |
| Maximum Take-off Weight | 13,500 kg |
Development and Testing
The Tejas, from its inception, was a result of the collaborative efforts of the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) of the Indian Department of Defence, with HAL as the prime industrial contractor. Testing has been extensive. As of December 2019, the Tejas had completed 4,599 test flights, reaching speeds of up to Mach 1.4.
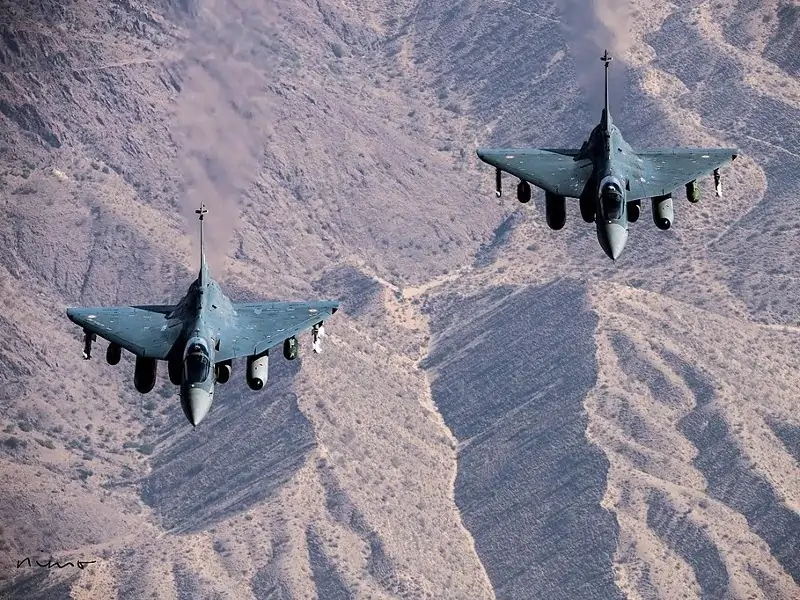

The developmental journey began with the first LCA Demonstrator I aircraft taking its maiden flight in January 2001, followed by the LCA Demonstrator II in June 2002. Subsequently, the second prototype vehicle (PV-II) had its first flight in December 2005, and the third in December 2006. The Indian Government’s approval of limited series production of 20 Tejas for the Air Force in April 2006 marked a significant milestone.
The first flight of the production aircraft was undertaken in April 2007, with the Tejas trainer variation’s first flight following in November 2009. Over the years, more prototypes and limited series production aircraft entered the fray, such as the LSP-4 and LSP-7. December 2013 marked another significant achievement when the Tejas successfully fired an infrared-seeking air-to-air missile during weapon release flight tests, thus achieving the Initial Operational Clearance (IOC) in the same year.
Operational Integration and Naval Prototypes
In October 2014, the first series-production aircraft successfully completed its maiden flight and was handed over to the Indian Air Force in January 2015. The second series production (SP2) aircraft successfully completed its maiden flight in March 2016. These successes paved the way for the Tejas to become an integral part of the Indian Air Force.
The Tejas were not limited to land operations. In April 2012, the naval prototype completed its maiden flight, and by July 2016, HAL handed over the first two Tejas aircraft to the Indian Air Force (IAF). The development of carrier-borne Tejas in single-seat and two-seat versions was granted approval in 1999. The carrier variant, designed with retractable canards and an adjustable vortex control, is intended to replace the fleet of Sea Harriers.
Hot Weather Flight Trials and Future Plans
The Indian Air Force started the second phase of hot weather flight trials on the Tejas fighter jet in June 2010. The tests carried out at temperatures up to 45°C, examined the digital flight control computer, avionics systems, multimode radar, RWR, and electrical and environmental control systems.
Looking ahead, the ADA conducted a conceptual design study of the ADA medium-combat aircraft, an advanced, stealth version of the Tejas, intended to replace the IAF Jaguar and Mirage 2000 fleet. This version boasts two engines with fully vectoring nozzles and no vertical or horizontal tail.
Orders and Deliveries
The Indian Air Force has ordered 40 Tejas aircraft, including 20 Tejas Mk1 and 20 Tejas Mk2. The first 20 fighters are built according to Initial Operational Clearance (IOC) standards, and the remaining will be built into the Final Operational Clearance (FOC) configuration. The Tejas Mk2’s maiden test flight is scheduled for 2022. By July 2017, the IAF had received four Tejas Mk1 aircraft. The Mk1 version received the FOC in February 2019.
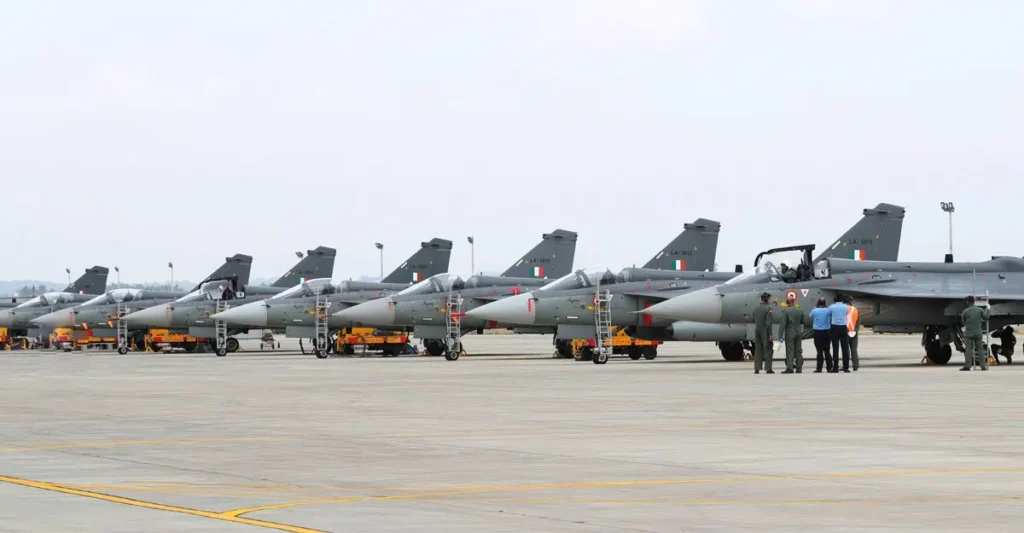

In November 2016, the Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) of India cleared the acquisition of 83 Tejas Mk1A variants, bringing the total number of orders to 123.
Design and Construction
The Tejas has a delta platform design with shoulder-mounted delta wings. It features a fin but no horizontal tail. The aircraft’s construction incorporates lightweight materials, including aluminum, lithium, titanium alloys, and carbon composites. The wing structure includes composite spars and ribs with a carbon fiber-reinforced plastic skin.
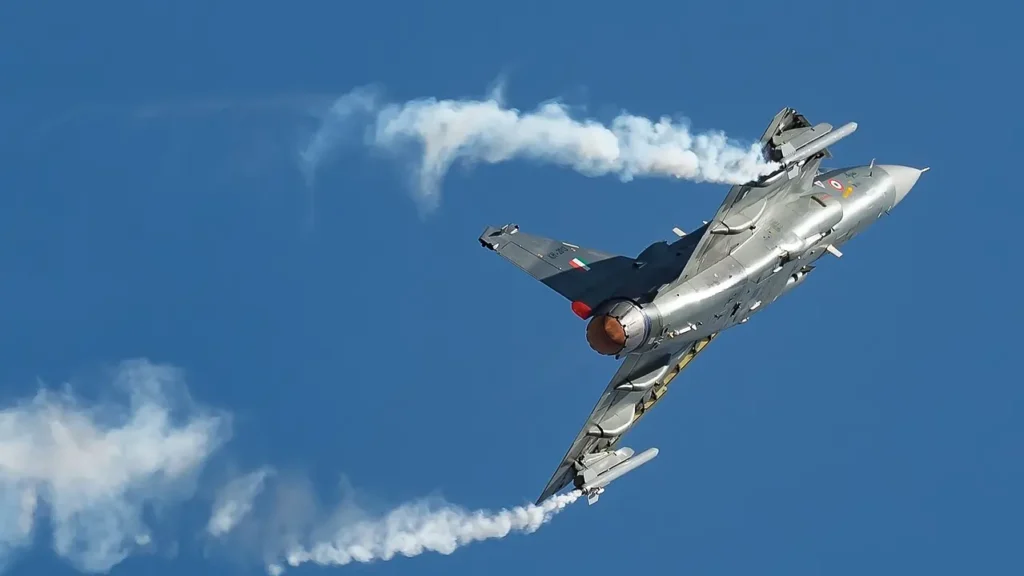

Bangalore-based National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL) designed and is responsible for the production of the fin and the rudder, as well as the construction of the aircraft fuselage.
Cockpit and Avionics
The Tejas is fitted with a night vision-compatible glass cockpit with Martin Baker (UK) zero-zero ejection seats. The cockpit boasts two 76mm × 76mm color liquid crystal multifunction displays developed by Bharat Electronics, a head-up display developed by the government-owned Central Scientific Instruments Organisation (CSIO) in Chandigarh, and a liquid crystal return-to-home-base panel and keyboard.
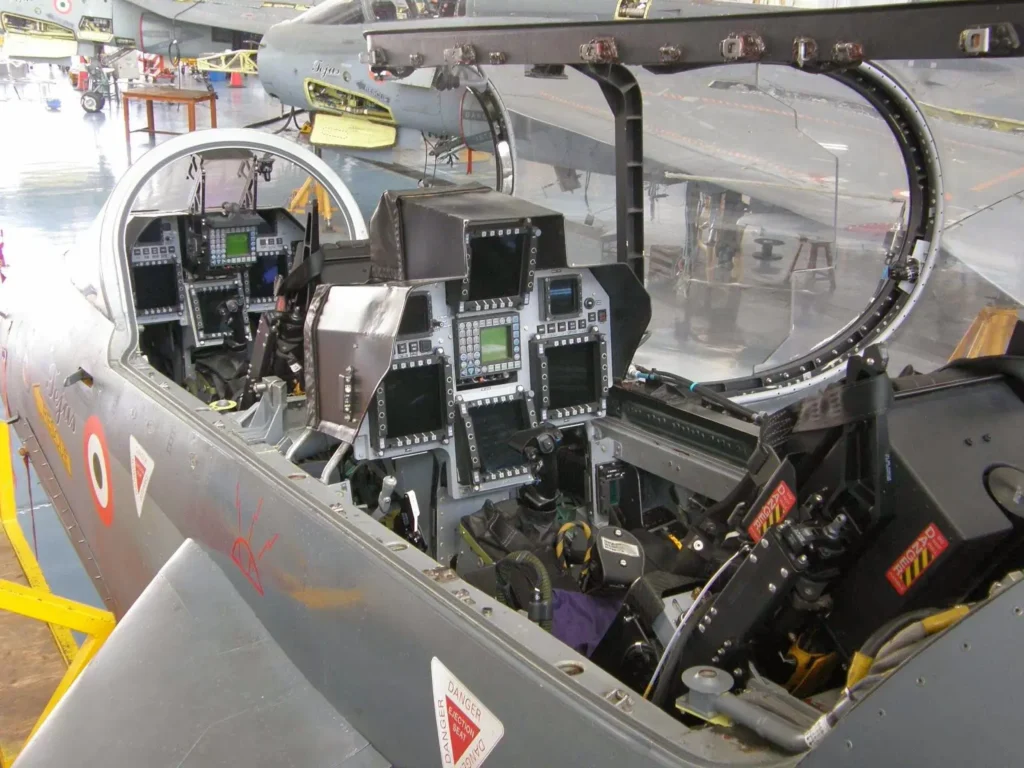

A helmet-mounted display and sight (HMDS) are also included, while the hands-on throttle and stick control system minimizes pilot workload and maximizes situational awareness. The navigation suite includes a Sagem SIGMA 95N ring laser gyroscope inertial navigation system with an integrated global positioning system.
Weapons and Countermeasures
The Tejas fighter aircraft is equipped with eight external hardpoints to carry stores, with three under each wing, one on the center fuselage, and one installed under the air intake on the port side. It is armed with air-to-air, air-to-ground, and anti-ship missiles, precision-guided munitions, rockets, and bombs. Electronic warfare, targeting, surveillance, reconnaissance, or training pods can be carried on the hardpoints. Drop tanks can also be carried.
The aircraft has a 23mm twin-barreled GSh-23 gun with a burst firing rate of 50 rounds a second and muzzle velocity of 715m a second, installed in a blister fairing under the starboard air intake. In October 2007, the aircraft successfully test-fired the R-73 air-to-air missile. The Vympel R-73 (NATO code name AA-11 Archer) missile is an all-aspect short-range missile with cooled infrared homing.
The Indian Government purchased Derby beyond-visual-range air-to-air missiles (BVR-AAM) from Rafael Advanced Defence Systems to incorporate into 200 aircraft. The Derby missile can engage targets at a range of 50km.
Sensors and Radar
The aircraft’s electronic warfare suite, developed by the Advanced Systems Integration and Evaluation Organisation (ASIEO) of Bangalore, includes a radar warning receiver and jammer, laser warner, missile approach warner, and chaff and flare dispenser. Electronics Research and Development Establishment and HAL have jointly developed the aircraft’s multimode radar.
The radar has multiple target search track-while-scan and ground-mapping modes of operation. It includes pulse Doppler radar with Doppler beam shaping, moving target indication, and look-up / look-down capability. The radar is mounted in a Kevlar radome. Saab is offering a sensor package for the Mk1A variant of the Tejas LCA. The package includes airborne electronically scanned array (AESA) fighter radar technology and an electronic warfare (EW) suite.
Engines and Performance
The prototype development aircraft are fitted with General Electric F404-GE-F2J3 turbofan engines with afterburn. Production versions are fitted with one General Electric 85kN F404-GE-IN20 turbofan engine with full authority digital engine control. A new turbofan engine, the GTX-35VS Kaveri, developed by Gas Turbine Research Establishment, was originally intended to power the production aircraft, but delays in development led to the purchase of the General Electric engines.
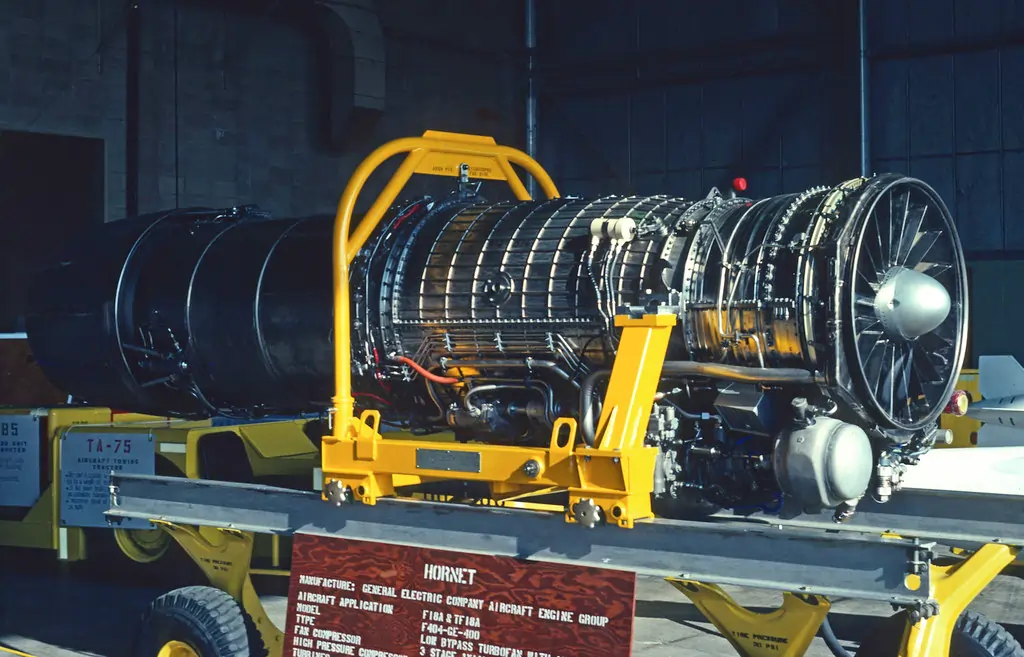
Snecma-Larzac has been chosen as the industrial partner in engine development. The Kaveri engine develops 52kN dry power and 80.5kN with afterburn, with Y-duct air intakes. The aircraft uses multi-axis thrust vectoring nozzles.
The Tejas LCA has wing and fuselage tanks and an in-flight refueling probe on the front starboard side. Drop tanks with a capacity of up to 4,000l can be carried on the inner and mid-board wing and fuselage centerline hard points. The aircraft is also fitted with a HAL gas turbine starter unit model GTSU-110.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Tejas Light Combat Supersonic Fighter stands as a testament to India’s growing prowess in the field of indigenous defense technology. With its robust design, advanced features, and successful integration into the Indian Air Force, the Tejas represents a significant achievement in the country’s defense capabilities. As India continues to refine and expand its military technology, the Tejas serve as a shining example of what the nation can achieve.

Read More Articles
- Why Cyber Security is Essential: Exploring 5 Key Reasons
- Astra Space’s Financial Struggles: A Close Brush with Bankruptcy
- Introducing the Xogdor Rocket to the Military Realm
- The Formation of the LEO Owner Operators Affinity Group
- Expanding Satellite-to-Smartphone Connectivity
- Navigating Privacy and Safety in Adult Webcam Streaming
- Choosing Between Open Source and Proprietary LLMs
- Rethinking Food Packaging for a Sustainable Future
- Mastering Typography in Web Design
- Exploring Typography Trends for Digital Design in 2024
- Unlocking Sustainable Economic Growth Through Innovation
- Navigating the Financial Landscape of Executive Education and MBA Programs
- Understanding Information Technology: The Backbone of Modern Business
- Understanding Algorithms: Definition, Functionality, and Real-Life Applications
- Understanding Machine Learning: A Comprehensive Exploration
- Unlocking the Power of Machine Vision: Revolutionizing Industries
- Unlocking the Power of Expert Systems: Enhancing Decision-Making with AI
- Unlocking the Power of Natural Language Processing
- Unlocking the Secrets of Artificial Intelligence
- Optimizing Logistics with AI: Revolutionizing Efficiency in Package Routing
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Tejas Light Combat Supersonic Fighter?
The Tejas is a single-seat, single-engine, lightweight, high-agility supersonic fighter aircraft developed by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL). It entered service with the Indian Air Force (IAF) in July 2016. The aircraft is designed for air superiority, ground attack, and maritime roles. The Tejas project was initiated to replace the aging MiG-21 fighters.
How was the Tejas Light Combat Supersonic Fighter developed?
The Tejas project was led by the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) of the Indian Department of Defence, with Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) as the prime industrial contractor. The development of the Tejas involved extensive testing, with the aircraft completing 4,599 test flights as of December 2019.
What is the history of the Tejas Light Combat Supersonic Fighter’s development?
The journey of the Tejas began with the first LCA Demonstrator I aircraft taking its maiden flight in January 2001, followed by the LCA Demonstrator II in June 2002. The second prototype vehicle (PV-II) had its first flight in December 2005, and the third in December 2006. The Indian Government’s approval of the limited series production of 20 Tejas for the Air Force in April 2006 marked a significant milestone.
What is the status of the operational integration of the Tejas Light Combat Supersonic Fighter?
The Tejas became an integral part of the Indian Air Force when the first series-production aircraft completed its maiden flight in October 2014. HAL handed over the first two Tejas aircraft to the Indian Air Force (IAF) in January 2015. Additionally, the naval prototype completed its maiden flight in April 2012.
What are the unique features of the Tejas Light Combat Supersonic Fighter?
The Tejas has a delta platform design with shoulder-mounted delta wings, featuring a fin but no horizontal tail. It is constructed using lightweight materials, including aluminum, lithium, titanium alloys, and carbon composites. The aircraft is equipped with a night vision-compatible glass cockpit and Martin Baker (UK) zero-zero ejection seats.
What armaments and countermeasures does the Tejas Light Combat Supersonic Fighter have?
The Tejas fighter aircraft is equipped with eight external hardpoints to carry stores. It is armed with air-to-air, air-to-ground, and anti-ship missiles, precision-guided munitions, rockets, and bombs. The aircraft has a 23mm twin-barreled GSh-23 gun with a burst firing rate of 50 rounds a second and muzzle velocity of 715m a second. Additionally, it has an electronic warfare suite developed by the Advanced Systems Integration and Evaluation Organisation (ASIEO) of Bangalore.
What is the current status of orders and deliveries of the Tejas Light Combat Supersonic Fighter?
The Indian Air Force has ordered 40 Tejas aircraft, including 20 Tejas Mk1 and 20 Tejas Mk2. The first 20 fighters are built according to Initial Operational Clearance (IOC) standards, and the remaining will be built into the Final Operational Clearance (FOC) configuration. By July 2017, the IAF had received four Tejas Mk1 aircraft. The Mk1 version received the FOC in February 2019. In November 2016, the Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) of India cleared the acquisition of 83 Tejas Mk1A variants, bringing the total number of orders to 123.
What are the specifications and performance capabilities of the Tejas Light Combat Supersonic Fighter?
The Tejas LCA has wing and fuselage tanks and an in-flight refueling probe on the front starboard side. Drop tanks with a capacity of up to 4,000l can be carried on the inner and mid-board wing and fuselage centerline hard points. The aircraft is also fitted with a HAL gas turbine starter unit model GTSU-110. It can fly at a maximum speed of 2,205km/h and a maximum altitude of 15,200m. The range of the aircraft is 3,000km, and the service ceiling is 16,500m. The aircraft weighs approximately 5,450kg and has a maximum take-off weight of 13,500kg.
What role does the Tejas Light Combat Supersonic Fighter play in India’s defense strategy?
The Tejas Light Combat Supersonic Fighter plays a vital role in India’s defense strategy by providing the Indian Air Force with modern and domestically produced aircraft. The Tejas project has allowed India to become more self-reliant in defense production, reducing dependency on foreign suppliers. Additionally, the Tejas enhances India’s air defense capabilities, as it is a modern, multi-role combat aircraft designed to excel in various missions.
What are the future plans for the Tejas Light Combat Supersonic Fighter?
The Tejas Mk2’s maiden test flight is scheduled for 2022. The Indian Air Force will receive 83 Tejas Mk1A variants, bringing the total number of orders to 123. Looking ahead, the Tejas project aims to continue its development, with plans to refine and improve the aircraft’s capabilities further. The Tejas is a cornerstone of India’s defense strategy, and its future development is critical for maintaining air superiority and protecting India’s interests.


