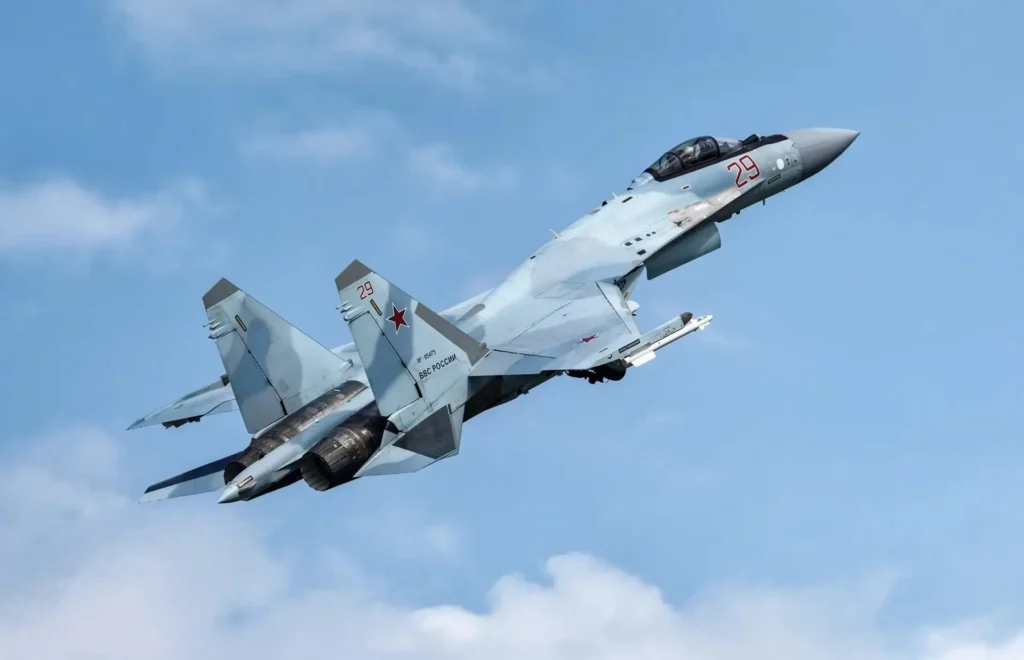
The Sukhoi Su-35BM, also known as the Su-35 Flanker-E, represents a remarkable advancement in multirole air superiority fighters. It is a product of extensive modernization from its predecessor, the Su-27. The latest iteration, the Su-35BM, which stands for “Bolshaya Modernization” (big modernization), boasts exceptional maneuverability, a high angle of attack, and a suite of high-capability weapon systems that enhance its dogfighting capabilities.
Table of Contents
Su-35 Flanker-E Specifications
| Specifications: | Details: |
|---|---|
| Type | Multirole Fighter |
| Developed From | Su-27 |
| Maneuverability | +9g |
| First Flight | February 2008 |
| Introduction to Service | 2010 (Su-35S for the Russian Air Force) |
| Production | Sukhoi Design Bureau, KNAPPO |
| Cockpit | Single-seat |
| Ejection Seat | Zvezda K-36D-3.5E zero-zero ejection seat |
| Fly-by-Wire System | Quadruplex, digital |
| Displays | Two 230mmx305mm MFI-35 liquid crystal displays |
| Head-Up Display (HUD) | IKSh-1M with 20°x30° field of view |
| Communication Systems | Two VHF/UHF encrypted radio systems Jam-resistant military data link system |
| Navigation System | Digital map display, strap-down inertial navigation system, global positioning system |
| Front Fuselage Diameter | Increased to accommodate Irbis-E radar |
| Materials | High-strength, low-weight composite materials, carbon fiber, aluminum-lithium alloy |
| Hardpoints | 12 (4 on each wing, 2 under the fuselage, 1 under each engine) |
| Air-to-Air Missiles | R-27, R-77, R-73E |
| Air-to-Surface Missiles | Kh-29, Kh-31P, Kh-58UShE |
| Anti-Ship Missiles | Kh-31A, Kh-59MK, Kalibr, Yakhont |
| Guided Bombs | KAB-500Kr, KAB-500S-E, LGB-250, Kab-1500Kr, KAB-1500LG |
| Rockets | 80mm, 122mm, 266mm, 420mm |
| Electronic Warfare Suite | Radar warning, radar jammer, cooperative radar jamming system, missile approach warner, laser warner, chaff and flare dispenser |
| Gun | Gryazev-Shipunov 30mm GSh-30-1 with 150 rounds of ammunition |
| Radar | Irbis-E multimode phased array 900mm passive phased array antenna Mechanical steering with electronic steering Radar Cross Section Detection: 0.01m² at ranges up to 90km Tracking: Up to 30 airborne targets with RCS of 3m² at ranges of 400km |
| Infrared Search and Track (IRST) | OLS-35 includes an infrared sensor, laser rangefinder, target designator, and television camera Acquisition Range: 50km forwards, 90km rearward Accuracy of the laser rangefinder: 5m CEP, up to 20km against airborne targets and 30km against ground targets |
| Engine | Sturn / UFA AL-31F 117S turbofan engines with thrust-vectoring nozzle control Total thrust: 172.6kN (86.3kN each) With afterburn: 284.4kN (142.2kN each) |
| Fuel Capacity | Internal: 14,350l Additional tailfin and fin-root tanks for increased unrefueled range and endurance External: 4,000l (2x PTB-2000) |
| Performance | Speed: Maximum: 2,390 km/h Range: Normal: 3,600 km Ferry: 4,200 km Altitude: Maximum: 18,000 m |
| Weights | Empty: 18,400 kg Max Takeoff: 34,500 kg |
Development of the Su-35
The Su-35BM was unveiled to the world at the Aerosalon MAKS air show in Moscow in August 2007, and it took its inaugural flight in February 2008. The Su-35BM was then introduced into serial production as the Su-35S for the Russian Air Force in 2010. The Sukhoi Design Bureau, located in Moscow, spearheaded the development, testing, and introduction of the Su-35 into serial production. KNAPPO of Komsomolsk-on-Amur carried out the manufacturing, both entities being part of the Sukhoi Aviation Holding Joint Stock Company.

Flight tests commenced on 18 February 2008. However, during high-speed ground tests in April 2009, the third prototype of the Su-35 program tragically crashed at Komsomolsk-on-Amur. The crash damaged the new NIIP Irbis-E radar set installed on the Su-35.
Orders and Deliveries
In August 2009, the Russian Air Force placed an order for 48 Sukhoi Su-35S jets, with deliveries scheduled to run until 2015. Manufacturing began in November 2009, with Sukhoi producing the components required for the assembly of the aircraft. The Su-35S is equipped with an information management system integrated with onboard subsystems and a new phased array radar system with long-range aerial target detection.
The first Su-35S aircraft was handed over to the 929th State Flight Test Centre (GLITS) for flight tests in August 2011. The Russian Ministry of Defence received six Su-35S production aircraft from Sukhoi in December 2012. In 2015, China ordered 24 Su-35S aircraft for China’s People’s Liberation Army Air Force, and in February 2018, the Indonesian Air Force placed an order for 11 Su-35S fighter jets.
Design and Cockpit
The Su-35 has a length of 21.9m, a wingspan of 15.3m, and a height of 5.9m. It can carry a maximum payload of 8,000kg, and the aircraft can be operated by one person.

The cockpit is equipped with a central control column and a Zvesda K-36D-3.5E zero-zero ejection seat, which allows the pilot to eject at zero speed and at zero altitude. The aircraft boasts a quadruplex, digital fly-by-wire control developed by the Avionika Moscow Research and Production Complex JSC (MNPK Avionika).
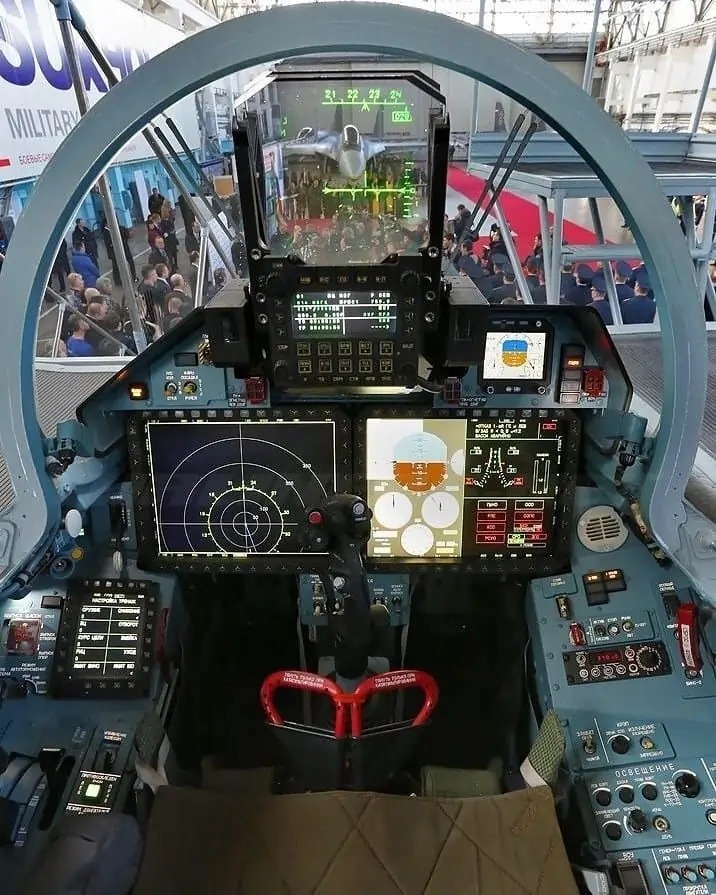

The cockpit features two 230mmx305mm high-resolution MFI-35 liquid crystal displays with a multifunction control panel and an IKSh-1M head-up display with a wide 20°x30° field of view. The pilot has two VHF/UHF encrypted radio communications systems and a jam-resistant military data link system between squadron aircraft and between the aircraft and ground control. The navigation system is based on a digital map display with a strap-down inertial navigation system and a global positioning system.
Construction Based on Su-27
Compared to the Su-27 design from which it is derived, the front fuselage diameter of the Su-35 has been increased to accommodate the larger 900mm-diameter antenna of the Irbis-E radar. High-strength, low-weight composite materials have been used for non-structural items such as radomes, nose wheels, doors, and leading-edge flaps. Some of the fuselage structures are made of carbon fiber and aluminum-lithium alloy.
Weapons
The Su-35 aircraft has 12 hardpoints for carrying external weapons and stores. Each wing has four hardpoints – one on the wingtip and three under-wing stations. There are two hard points on the underside of the fuselage on the centerline and one under each engine.
The aircraft’s air-to-air missiles can include the Vympel R-27 (NATO designation AA-10 Alamo), the Vympel radar-guided medium-range R-77 (AA-12 Adder), and the Vympel short-range infrared-guided R-73E (AA-11 Archer).
The aircraft’s air-to-surface missiles include the Molniya Kh-29 (AS-14 Kedge) tactical missiles, the Kh-31P (AS-17 Krypton) anti-radiation missiles, and the long-range Kh-58UShE (AS-11 Kilter) anti-radiation missiles.
The Su-35’s anti-ship missiles include Kh-31A, the long-range Kh-59MK (AS-18 Kazoo), the long-range Kalibr, and the NPO Mashinostroenia heavy long-range Yakhont missile.
Ordnance
The Su-35 can be armed with a range of guided bombs, including the KAB-500Kr TV-guided bomb, KAB-500S-E satellite-guided bomb, LGB-250 laser-guided bomb, Kab-1500Kr TV-guided bomb, and KAB-1500LG laser-guided bomb. The aircraft can also be armed with 80mm, 122mm, 266mm, and 420mm rockets.
Countermeasures and Guns
The aircraft’s electronic warfare suite includes a radar warning system, radar jammer, cooperative radar jamming system, missile approach warner, laser warner, and chaff and flare dispenser. The Gryazev-Shipunov 30mm GSh-30-1 gun is fitted in the starboard wing root with 150 rounds of ammunition.
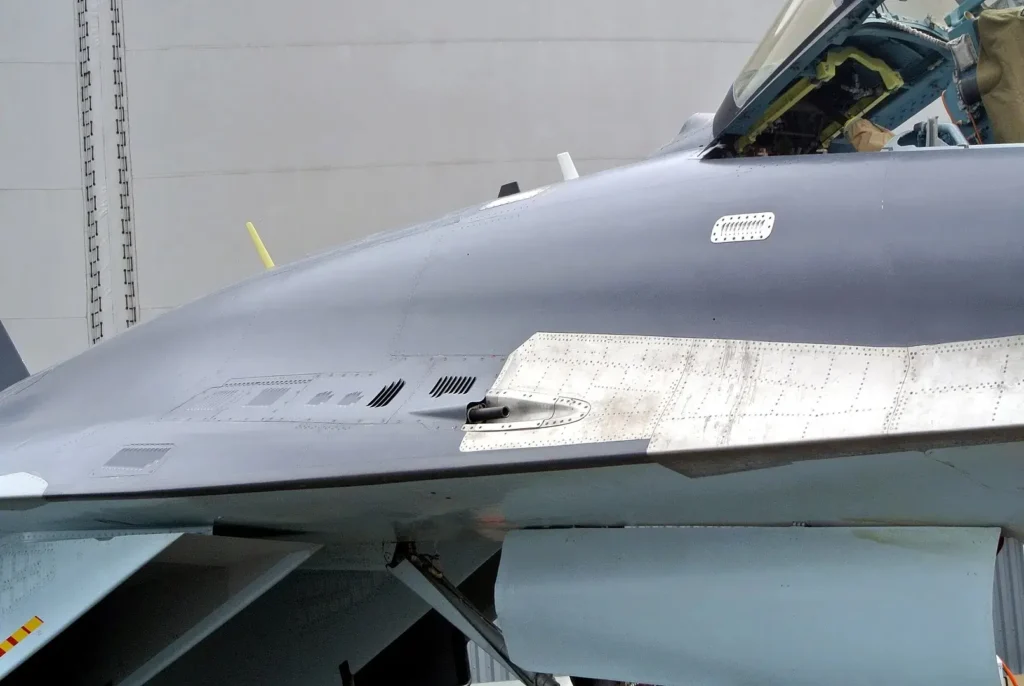

Sensors
The X-band multimode phased array Irbis-E radar is supplied by Tikhomirov Scientific-Research Institute of Instrument Design (NIIP), based in Zhukovsky. Irbis-E is a high-performance radar designed for the Su-35 aircraft.
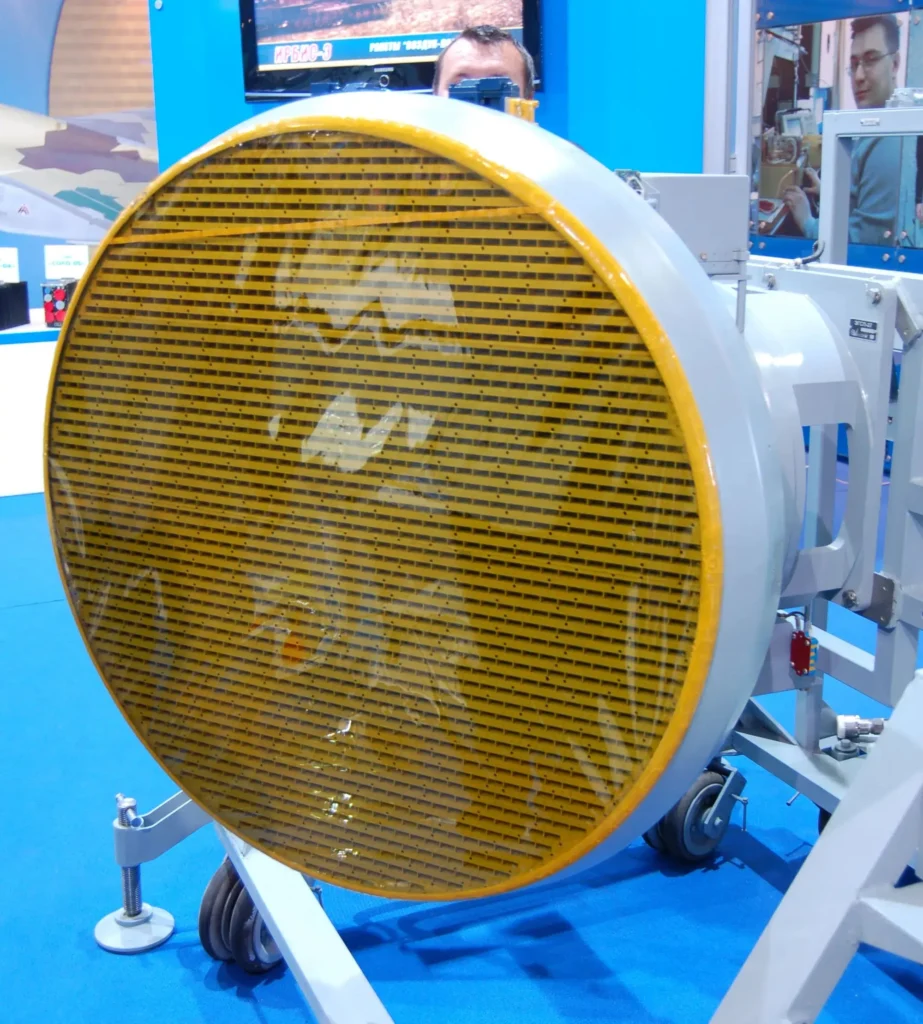

The 900mm passive phased array antenna is mounted on a hydraulic actuator for mechanical steering. The electronic steering provides azimuthal and elevation coverage of 60°. With both mechanical and electronic scanning, the coverage is 120°.
The radar can detect low-observable and stealth aircraft, unmanned air vehicles, and missiles with a radar cross-section of 0.01m² at ranges up to 90km. Radar modes include air-to-air, air-to-ground, air-to-sea, mapping, Doppler beam, and synthetic aperture radar modes. It can detect and track up to 30 airborne targets with a radar cross-section (RCS) of 3m² at ranges of 400km using track-while-scan mode.
Infrared Search and Track
The infrared search and track fire control system, OLS-35 IRST, includes an infrared sensor, laser rangefinder, target designator, and television camera. The accuracy of the laser rangefinder is 5m CEP (circular error probability), to a maximum range of 20km against airborne targets and 30km against ground targets. The OLS-35 is a high-performance system with ±90° azimuthal and +60°/-15° elevation coverage.
The system’s acquisition range against a non-afterburning target is 50km forward and 90km rearward. The Su-35 can also be fitted with a UOMZ Sapsan targeting and laser designation pod.
Engine and Performance
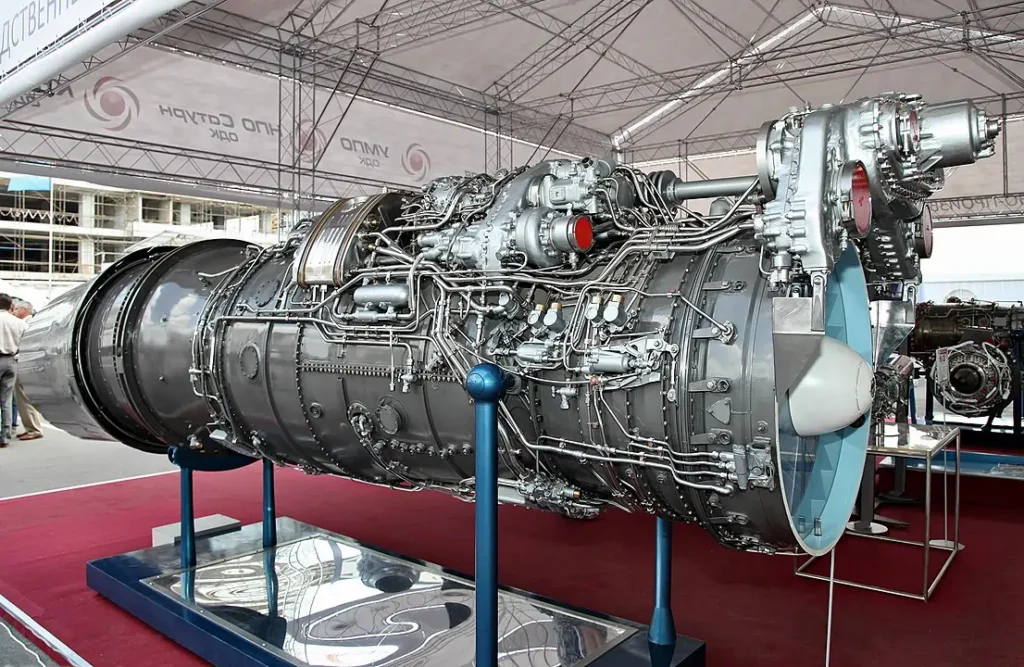
The aircraft is powered by two Sturn / UFA AL-31F 117S turbofan engines with thrust-vectoring nozzle control, each supplying 86.3kN thrust or 142.2kN with afterburn. The engines were developed jointly by Sukhoi, Saturn, and UMPO.
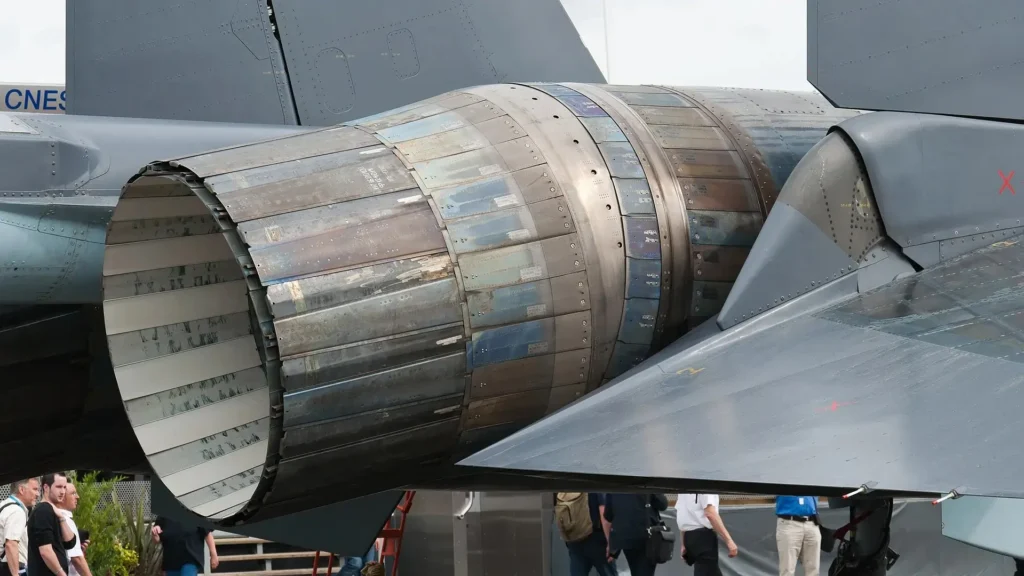

The total fuel capacity is 14,350l. To increase the unrefueled range and endurance compared to earlier models, the Su-35 incorporates additional tailfin and fin-root tanks. The fuel tanks are of aluminum-lithium construction and are located in the wings, fuselage, and square-tip twin tailfins. The unrefueled range on internal fuel is 1,580km.
For in-flight refueling, the aircraft is equipped with a refueling probe on the port side of the nose. Two external fuel tanks, type PTB-2000, provide an additional 4,000l of fuel. The ferry range with two external tanks is 4,500km.
The aircraft can fly at a maximum speed of 2,390km/h. The normal and ferry ranges of the aircraft are 3,600km and 4,200km, respectively. The maximum altitude is 18,000m. The Su-35 weighs around 18,400kg, and the maximum take-off weight is 34,500kg.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Su-35 Flanker-E represents the apex of modern aerial warfare technology. With its unrivaled combination of agility, firepower, and advanced avionics, this multi-role fighter stands ready to meet the challenges of the 21st-century battlefield. As it continues to serve alongside allied air forces worldwide, the Su-35 reaffirms its status as a true titan of the skies.
Read More Articles
- US Air Force Successfully Conducts AI-Piloted Fighter Jet Dogfights
- Russian Su-35 Fighters Equipped with Stealth X-69 ALCMs
- Why Cyber Security is Essential: Exploring 5 Key Reasons
- Astra Space’s Financial Struggles: A Close Brush with Bankruptcy
- Introducing the Xogdor Rocket to the Military Realm
- The Formation of the LEO Owner Operators Affinity Group
- Expanding Satellite-to-Smartphone Connectivity
- Navigating Privacy and Safety in Adult Webcam Streaming
- Choosing Between Open Source and Proprietary LLMs
- Rethinking Food Packaging for a Sustainable Future
- Mastering Typography in Web Design
- Exploring Typography Trends for Digital Design in 2024
- Unlocking Sustainable Economic Growth Through Innovation
- Navigating the Financial Landscape of Executive Education and MBA Programs
- Understanding Information Technology: The Backbone of Modern Business
- Understanding Algorithms: Definition, Functionality, and Real-Life Applications
- Understanding Machine Learning: A Comprehensive Exploration
- Unlocking the Power of Machine Vision: Revolutionizing Industries
- Unlocking the Power of Expert Systems: Enhancing Decision-Making with AI
- Unlocking the Power of Natural Language Processing
- Unlocking the Secrets of Artificial Intelligence
- Optimizing Logistics with AI: Revolutionizing Efficiency in Package Routing
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Su-35 Flanker-E Multirole Fighter?
The Su-35 Flanker-E Multirole Fighter, officially known as the Sukhoi Su-35BM (Su-35S), is an advanced capability air superiority fighter developed from the Su-27 by the Sukhoi Design Bureau in Moscow. It is designed to provide high maneuverability, boasting a capability of up to +9g and a high angle of attack. Equipped with high-capability weapon systems, the Su-35 excels in dogfighting situations and carries advanced air-to-air and air-to-surface missiles, making it a formidable multirole fighter.
When was the Su-35 Flanker-E Multirole Fighter first introduced?
The Su-35 Flanker-E Multirole Fighter, known as the Su-35BM (Su-35S), was first unveiled at the Aerosalon MAKS air show in Moscow in August 2007. Its maiden flight took place in February 2008, and it entered serial production as the Su-35S for the Russian Air Force in 2010.
What is the maximum speed of the Su-35 Flanker-E Multirole Fighter?
The Su-35 Flanker-E Multirole Fighter can fly at a maximum speed of 2,390 kilometers per hour (1,485 miles per hour). This exceptional speed allows for rapid response and engagement during missions, enhancing its air superiority capabilities.
How many hard points does the Su-35 Flanker-E Multirole Fighter have?
The Su-35 Flanker-E Multirole Fighter is equipped with a total of 12 hardpoints for carrying external weapons and stores. Each wing has four hardpoints, one on the wingtip, and three under-wing stations. Additionally, there are two hard points on the underside of the fuselage on the centerline and one under each engine.
What are the dimensions of the Su-35 Flanker-E Multirole Fighter?
The Su-35 Flanker-E Multirole Fighter has a length of 21.9 meters (72 feet), a wingspan of 15.3 meters (50 feet), and a height of 5.9 meters (19 feet). With the capacity to carry a maximum payload of 8,000 kilograms, the Su-35 Flanker-E is operated by one person, making it highly efficient and versatile.
How many Su-35 Flanker-E Multirole Fighters did the Russian Air Force order?
The Russian Air Force placed an order for 48 Sukhoi Su-35S jets in August 2009, with deliveries scheduled to run until 2015. Sukhoi began producing the components required for the assembly of the aircraft in November 2009. The first Su-35S aircraft was handed over to the 929th State Flight Test Centre (GLITS) for flight tests in August 2011, and the Russian Ministry of Defence received six Su-35S production aircraft from Sukhoi in December 2012.
What are some of the Su-35 Flanker-E Multirole Fighter’s air-to-air missiles?
The Su-35 Flanker-E Multirole Fighter’s air-to-air missiles include the Vympel R-27 (NATO designation AA-10 Alamo), the Vympel radar-guided medium-range R-77 (AA-12 Adder), and the Vympel short-range infrared-guided R-73E (AA-11 Archer). These missiles provide the Su-35 with effective capabilities for engaging aerial threats at various ranges.
What are some of the Su-35 Flanker-E Multirole Fighter’s air-to-surface missiles?
The Su-35 Flanker-E Multirole Fighter’s air-to-surface missiles include the Molniya Kh-29 (AS-14 Kedge) tactical missiles, the Kh-31P (AS-17 Krypton) anti-radiation missiles, and the long-range Kh-58UShE (AS-11 Kilter) anti-radiation missiles. These missiles enable the Su-35 to engage ground and surface targets with high precision and effectiveness.
What type of engine powers the Su-35 Flanker-E Multirole Fighter?
The Su-35 Flanker-E Multirole Fighter is powered by two Sturn / UFA AL-31F 117S turbofan engines with thrust-vectoring nozzle control, each supplying 86.3 kilonewtons (kN) of thrust or 142.2 kN with afterburn. These engines, developed jointly by Sukhoi, Saturn, and UMPO, provide the Su-35 with exceptional speed and agility, enhancing its performance in various mission scenarios.
What is the maximum take-off weight of the Su-35 Flanker-E Multirole Fighter?
The Su-35 Flanker-E Multirole Fighter weighs around 18,400 kilograms (40,565 pounds), and the maximum take-off weight is 34,500 kilograms (76,060 pounds). With its additional tailfin and fin-root tanks, the Su-35 Flanker-E boasts increased unrefueled range and endurance compared to earlier models, making it an even more versatile and formidable aircraft.


